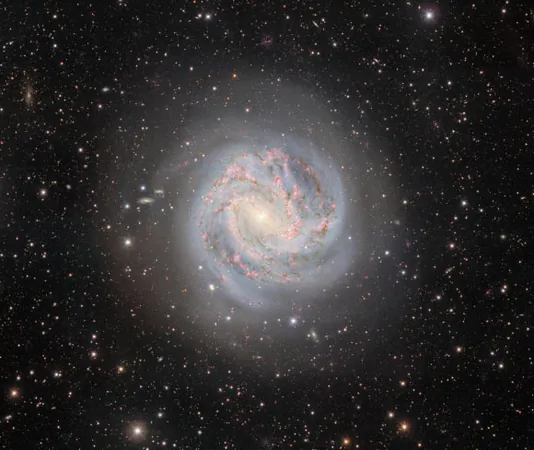

A Breathtaking Snapshot of the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy: Messier 83 Revealed
2024-12-09
Author: Jacob
Astonishing Astrophotography
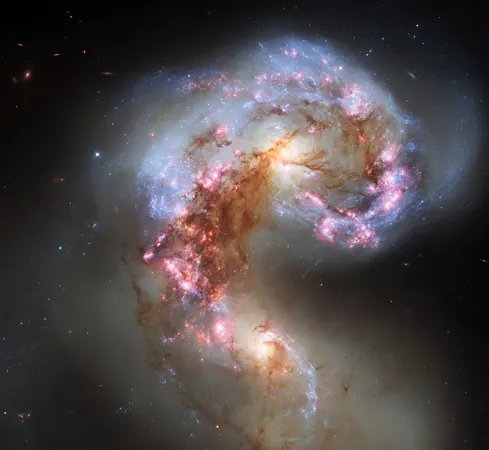
In an astonishing feat of astrophotography, the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) has unveiled a stunning new image of Messier 83, also known as the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy. This striking spiral galaxy, located about 15 million light-years away in the southern constellation of Hydra, is renowned for its vibrant star formation rates and intriguing cosmic phenomena.
Overview of Messier 83
Messier 83, characterized by its magnificent swirling spiral arms, measures approximately 50,000 light-years in diameter, making it about half the size of our Milky Way. It is one of the brightest spiral galaxies visible in the night sky, boasting an apparent magnitude of 7.5. For stargazers, the best time to observe this celestial wonder is in May, where a pair of binoculars can provide a decent view.
Astronomical Significance
The galaxy's nearly face-on orientation as seen from Earth allows astronomers to explore its spiral structure in remarkable detail. Messier 83 is a standout member of the Centaurus A/M83 Group, which includes other fascinating galaxies like the dusty NGC 5128.
Historical Discovery
This cosmic marvel was first discovered by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in February 1752 during his expedition to the Cape of Good Hope. Lacaille cataloged numerous stars and nebulous objects during this period, including Messier 83, which Charles Messier would later include in his famous catalog in 1781. At that time, the understanding of galaxies was limited, with Messier referring to it as 'a nebula without stars,' prior to Edwin Hubble's groundbreaking work that identified such objects as distant galaxies.
Latest Imaging and Findings
The latest image of Messier 83 highlights its beautifully defined spiral arms, rich with pink clouds of hydrogen gas—indicators of vigorous new star formation. Interspersed within these vibrant regions are clusters of bright blue stars, which emit intense ultraviolet radiation strong enough to clear out the surrounding gas. At the galaxy's core, a yellow central bulge composed of older stars is connected by a weak bar that channels gas from the outskirts toward the center, further fueling the star-making process.
Intriguing Stellar Activities
What makes Messier 83 even more intriguing is its history of supernovae; astronomers have documented six stellar explosions within the galaxy over the last century, a figure only matched by a couple of other galaxies. These events provide vital insights into the life cycles of stars and the dynamic nature of stellar evolution.
Possible Galactic Merger
In a surprising twist, astronomers uncovered a concentration of mass near the galaxy's center that resembles a second nucleus. This finding suggests that Messier 83 may be in the process of consuming another galaxy, a merger that could account for the heightened starburst activity observed. Researchers predict that the two nuclei, which likely harbor black holes, will eventually merge into a single nucleus in approximately 60 million years.
Conclusion and Future Implications
As scientists continue to probe the depths of Messier 83, the discoveries can offer profound insights into the workings of our universe, revealing the complex interplay of creation and destruction that shapes galaxies like our own. Stay tuned for more breathtaking celestial revelations as we explore the cosmos!
Don't Miss Out!
The universe is full of mysteries waiting to be uncovered! Discover more about galactic formations and what they could mean for our understanding of space.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)