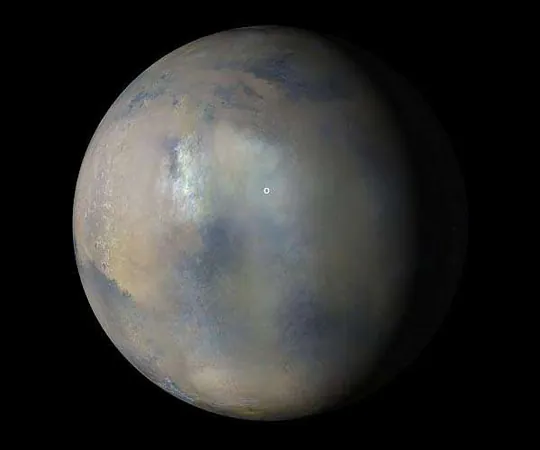

Are Mars Dust Storms the Key to Understanding Climate Change on the Red Planet?
2024-12-10
Author: Benjamin
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study released by a team of planetary scientists from the University of Colorado Boulder, new insights have emerged concerning the puzzling dust storms that often engulf Mars. These storms, capable of cloaking the entire planet, might actually be influenced by warming weather patterns on the Martian surface.
The Impact on Future Mars Missions
Lead researcher Heshani Pieris emphasized the urgency of comprehending these dust phenomena for the safety of future Mars missions. "Dust storms can severely disrupt the operations of rovers and landers on Mars. As we move toward potential crewed missions, this understanding becomes critical," stated Pieris, who is currently affiliated with the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) at CU Boulder. "The dust is light yet tricky; it adheres to everything, posing serious challenges."
The findings, which heavily rely on data gathered from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's observations, will soon be presented at the American Geophysical Union meeting in Washington, sparking excitement in the scientific community.
Exploring the Mechanisms Behind Martian Dust Storms
The study delved into the atmospheric conditions that precede nearly two-thirds of major Martian dust storms, particularly examining temperature fluctuations. Co-author Paul Hayne, an associate professor at LASP, pointed out significant gaps in the current understanding of Martian weather patterns. "To predict when smaller storms escalate into global ones, we need a clearer picture of the physics at play," said Hayne. "We're still piecing together the basic mechanics of how these storms initiate."
Interestingly, many dust storms arise near Mars' polar ice caps during the latter part of its year when conditions are optimal for expansion. Though Mars' thin atmosphere means that windy forces are minimal, the consequences of these storms can be dire. For example, NASA's Opportunity rover lost all functionality in 2018 during a global storm after its solar panels were engulfed in dust.
From Heat to Dust: The Connection
In an extensive analysis, Pieris and Hayne examined data collected over eight Martian years utilizing the Mars Climate Sounder instrument. Their research indicated that an impressive 68% of significant dust storms were preceded by a rise in surface temperatures.
"It's almost as if Mars must 'wait' for a clear atmospheric layer before unleashing a major dust storm," Hayne noted. While the correlation between temperature and dust storms does not establish a definitive cause-and-effect relationship, Pieris points out intriguing similarities to weather patterns on Earth. For instance, warm air at the surface can ascend to create storm clouds, a phenomenon that may also occur on Mars when the right conditions are met.
"As the surface heats, the air layer directly above it can become buoyant and rise, carrying dust into the atmosphere," she explained.
Looking Ahead: Future Predictive Models
Eager to enhance their predictive capabilities, the research team plans to analyze more current Martian weather data. They aspire to eventually predict storm occurrences using real-time information, a crucial tool for the next wave of exploratory missions to Mars.
"This study is not the final word on forecasting Martian storms," Pieris acknowledged. "But we aim to lay down the groundwork for future advancements in our understanding."
As curiosity about Mars and its potential for human exploration continues to grow, these findings could hold the key to unlocking further mysteries of the Red Planet while ensuring that future missions are well-prepared for the volatile Martian environment. Could understanding these dust storms lead to revolutionary discoveries about Mars' climate and our own? Time will tell!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)