Breakthrough Discovery: Astrocytes Could Hold the Key to Alzheimer's Treatment!
2024-09-30
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, a team of researchers led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has unveiled a promising new mechanism involving astrocytes that could revolutionize the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Collaborating with experts from the Institute for Basic Science and Boston University’s Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, the team has pinpointed a novel therapeutic target that leverages the brain's non-neuronal support cells, known as astrocytes.
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, characterized by the accumulation of toxic amyloid-beta (Aβ) proteins in the brain, leads to the degeneration of neurons and subsequent memory loss and cognitive decline. Historically, research efforts have concentrated on neuronal cells, yet this study shifts focus to the vital role astrocytes play in managing brain health.
Role of Autophagy
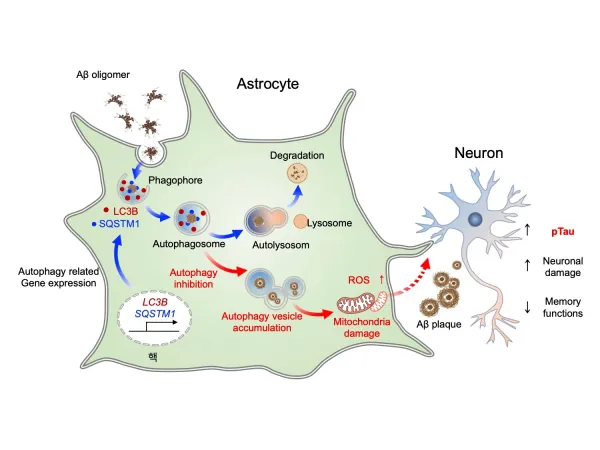
At the heart of the study is autophagy, a critical cellular process where cells degrade and recycle their components to maintain balance and facilitate recovery. Researchers discovered that in response to toxic protein accumulation in the brains of AD patients, astrocytes initiate the expression of genes responsible for autophagy. By transferring these genes specifically into astrocytes within AD mouse models, they witnessed a remarkable recovery of damaged neurons.
Key Findings
The findings are particularly staggering: activating astrocytic autophagy led to a reduction in Aβ aggregates and an improvement in memory and cognitive functions. When these autophagy-associated genes were expressed specifically in the hippocampus—a brain region crucial for memory—the researchers observed a significant decrease in neurological symptoms typical of Alzheimer’s.
Implications for Future Research
This pioneering research paves the way for a radical departure from traditional Alzheimer’s drug development, which has predominantly focused on neurons. Instead, it identifies astrocytes as an appealing and novel target for future therapeutic strategies. The research team aims to further investigate drug development that could enhance the autophagic processes in astrocytes, with the potential to prevent or mitigate the symptoms of dementia. Preclinical studies are on the agenda, holding promise for future Alzheimer's treatments.
Expert Insights
In a statement, Dr. Ryu, along with first author Dr. Suhyun Kim, emphasized the significance of their findings, declaring, “Our research highlights the potential of astrocytic autophagy in restoring neuronal health and cognitive functions in dementia-affected brains. We aspire to deepen our understanding of cellular mechanisms related to waste management in the brain, which could be the frontier for Alzheimer's research.
Conclusion
This innovative work not only contributes to the scientific community's understanding of neurodegenerative diseases but also opens the door to developing treatments that could reshape the future of Alzheimer’s care. With millions affected globally, breakthroughs like these instill hope in the fight against this devastating disease.
Future Outlook
Stay tuned as more developments arise in this promising realm of Alzheimer’s research!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)