
China's Groundbreaking Inflatable Module Successfully Tested in Space!
2024-11-26
Author: Benjamin
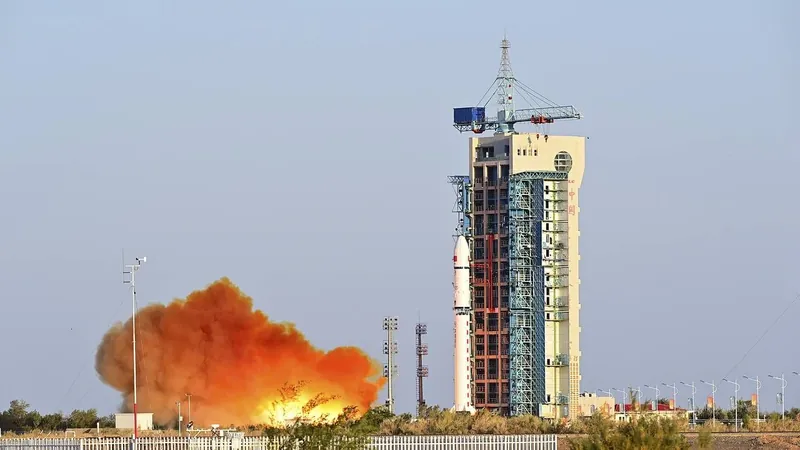
In a significant leap for space technology, China has recently tested a pioneering inflatable module during its Shijian-19 mission, a move that could transform future space exploration. This successful test was quietly executed in low-Earth orbit, as reported by Azernews.
The inflatable module, developed by the Chinese Academy of Space Technology (CAST), is crafted from advanced flexible composite materials. Initially compact and folded for launch, it showcases remarkable innovation by expanding once reaching its intended orbit. This shift to inflatable technology not only reduces weight but also increases packaging efficiency, which may revolutionize how structures are deployed in the harsh environment of space.
Chinese space authorities have confirmed that the module performed exceptionally well during its orbital test. A detailed statement revealed that extensive ground tests preceded the flight, ensuring the module's functionality through rigorous evaluations. These assessments included leak-proof testing, resistance to space debris, extreme pressure durability, vibration endurance, and thermal vacuum simulations. All results pointed towards a successful operation, building optimism for the module's future applications.
The implications of this technology are vast and potentially groundbreaking. The use of inflatable structures could signal an important evolution in the design of habitats for astronauts on missions to celestial bodies such as the Moon and Mars. In addition, these modules could enhance the functionality of existing space stations, permitting rapid deployment in orbit, which is vital for various commercial and scientific endeavors.
As nations ramp up their space exploration ambitions, China's successful test of the inflatable module not only showcases its technological advancements but also positions it as a key player in the new era of space exploration. The potential for these innovations to serve as expandable habitats could be the game-changer needed for ambitious future missions. Stay tuned for more updates as this technology develops!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)