
E-Tattoos: The Future of Brain Monitoring?
2024-12-09
Author: Jacob
Introduction
In the world of neuroscience, the quest for efficient, non-invasive brain monitoring has taken an exciting turn with the introduction of electronic tattoos, or "e-tattoos," which promise to revolutionize how we understand neural activity.
Traditional EEG Challenges
Traditionally, electroencephalography (EEG) has been the gold standard for recording electrical activity in the brain, crucial for diagnosing conditions like epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries. However, the conventional EEG setup is fraught with challenges.
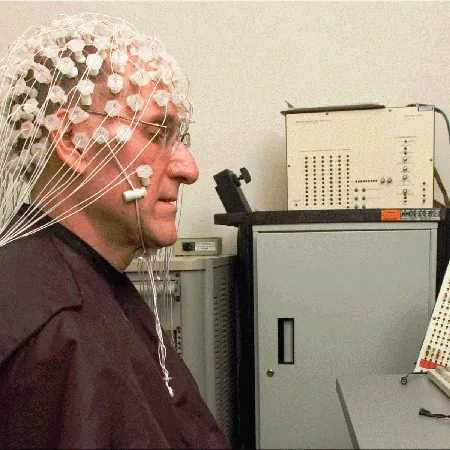
An EEG works by placing small metal discs known as electrodes on the scalp, using a conductive gel to ensure proper connection. The electrodes must be positioned with precision, typically 10 to 20 percent of the skull's distance apart, to obtain accurate readings. While EEG caps exist to streamline this process, varying head shapes can lead to misplacement and, consequently, inaccurate results. This is where EEG technicians come into play, meticulously adjusting electrode positions. Despite their expertise, the procedure can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
Additionally, once the electrodes are in place, patients are often required to remain motionless to prevent the electrodes from detaching, and the conductive gel can dry out, causing further complications. In prolonged EEG studies, such as those for epilepsy, alternative sticky adhesives are used, but they come with their own set of maintenance challenges.
Introduction of E-Tattoos
Enter e-tattoos, a cutting-edge solution that leverages advanced technology to overcome these limitations. By utilizing 3D scanning techniques and a sophisticated 5-axis microjet printing robot, e-tattoos allow for precise application of conductive ink directly onto the scalp.
This ink, developed from biocompatible polymers, is jetted through hair and dries into a flexible, stretchable film that creates a network of disc-shaped sensors and interconnecting lines to facilitate brain monitoring without the cumbersome traditional setups.
Benefits and Potential of E-Tattoos
Not only do e-tattoos promise greater accuracy in readings, but they also offer enhanced comfort for patients, allowing for more natural movement during tests.
This innovation could make long-term brain monitoring more feasible, opening doors for continuous assessment of neurological conditions and improved patient care.
As research and development in this field continue, the potential for e-tattoos extends beyond just medical diagnostics. They could play a pivotal role in neuroscience research, brain-computer interfaces, and even mental health monitoring, making them a fascinating area for further examination.
Conclusion
The dawn of e-tattoos signifies a significant leap forward in our approach to understanding the brain. As scientists explore this technology, it brings us one step closer to refining how we monitor and diagnose brain health—a thrilling prospect that could change the landscape of neurology forever. Stay tuned as we follow this exciting development in brain science!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)