
Epic Views of the Fedchenko Glacier Unveiled: A Glimpse into Central Asia's Frozen Wonder!
2024-11-18
Author: Benjamin
Epic Views of the Fedchenko Glacier Unveiled: A Glimpse into Central Asia's Frozen Wonder!
NASA’s Earth Observatory has recently spotlighted the breathtaking Fedchenko Glacier, perched majestically in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan. This marvel of nature is not only one of the longest glaciers outside of polar regions but also a vital player in the region's ecosystem.
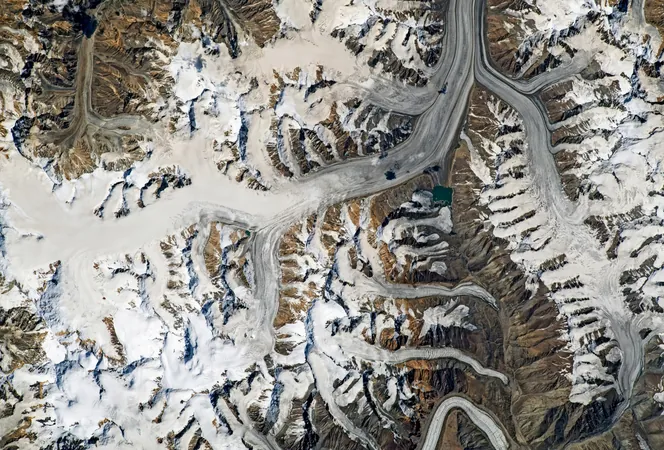
Captured in stunning detail by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station, the image highlights the glacier's intricate features, prominently displaying dark and light-brown parallel lines known as medial moraines. These stunning formations indicate the flow of ice down the valleys, created from debris the glacier has eroded from surrounding peaks.
The Glacier’s Magnitude and Importance
Stretching approximately 48 miles and covering around 270 square miles, the Fedchenko Glacier is a crucial reservoir of freshwater, supplying numerous rivers and influencing the hydrology of Central Asia. Interestingly, despite its location in a semi-arid region, the glacier thrives due to significant snowfall accumulating in the high altitudes of the Pamir peaks.
The glacier is named after Russian explorer Alexei Pavlovich Fedchenko, who first surveyed it in 1928 during Soviet expeditions. Today, scientists closely monitor its changes as indicators of the wider impacts of global warming, providing key insights into climate dynamics in the region.
The Grave Threat of Climate Change
Unfortunately, the grandeur of the Fedchenko Glacier is under siege from climate change, with rising global temperatures leading to its alarming retreat. Such glacial melt poses considerable risks to the region, threatening the water supply for millions who rely on glacial runoff for drinking, farming, and hydropower.
Pollution and human activities further exacerbate these risks. Urbanization and deforestation diminish reflective snow cover, hastening the melting process, while pollutants such as black carbon darken glacier surfaces, increasing heat absorption.
Consequences of Retreating Glaciers
The ramifications of melting glaciers extend beyond immediate water supply concerns. These changes contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems. The loss of glacial habitats also imperils the biodiversity that depends on these cold environments for survival.
Taking Action: Protecting Our Glaciers
To combat these urgent threats, concerted efforts are underway to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, preserving glacier regions from industrial exploitation, and encouraging sustainable tourism practices. However, swift and decisive actions are necessary to shield these magnificent glaciers from irreversible damage.
Discovering the Pamir Mountains
In addition to the glacier's ecological significance, the Pamir Mountains, known as the “Roof of the World,” encompass mesmerizing landscapes that span Tajikistan, Afghanistan, China, and Kyrgyzstan. This region, with its towering peaks above 7,000 meters, has long been essential for trade and cultural exchange, forming a crucial segment of the ancient Silk Road.
Today, the Pamirs draw trekkers and adventurers eager to experience their stunning beauty and challenging terrain. The mountains are not just a geographical marvel; they are also home to diverse communities with rich cultural traditions shaped by their majestic yet harsh environment.
Final Thoughts
The Fedchenko Glacier and the surrounding Pamir Mountains are emblematic of the critical environmental issues we face today. Protecting these natural wonders is not just about preserving beauty; it’s about ensuring a sustainable future for the millions who depend on these glaciers for survival.
Stay tuned for more captivating insights into our planet’s pristine environments—it’s a race against time to save them!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)