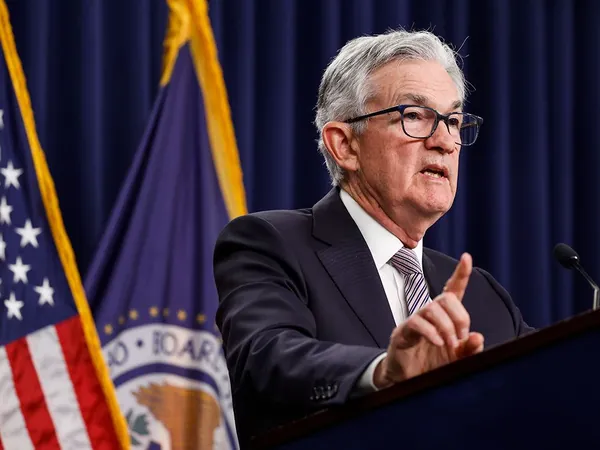

Federal Reserve Slashes Interest Rates Again: What It Means for Your Wallet
2024-12-18
Author: Emily
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cut Overview
In a significant move that has captured the attention of economists and consumers alike, the Federal Reserve announced a quarter-point cut in its key interest rate this Wednesday. This marks the third rate cut of the year, reflecting the Fed's ongoing efforts to navigate a complex economic landscape marked by persistent inflation.
Future Rate Cut Outlook
The decision comes as Fed officials indicate a more cautious outlook for future rate cuts. According to their latest projections, the central bank plans to reduce its benchmark rate only twice more in 2025, a notable drop from previous expectations of four cuts. This potentially signals that consumers might not experience as much relief in borrowing costs for mortgages, auto loans, and credit cards as previously hoped.
Current Benchmark Rate
The benchmark rate now stands at 4.3%, after significant cuts of half a point in September and a quarter-point last month. The Fed is gradually approaching what policymakers deem the 'neutral' interest rate—a level that neither stimulates nor slows down economic growth too much.
Inflation Challenges
One of the major challenges facing the Fed is the sticky nature of inflation. As of October, inflation remains stubbornly above the Fed's target of 2%, sitting at 2.8%. This persistent inflationary pressure complicates the central bank's efforts to foster a 'soft landing' for the economy, where rate adjustments effectively control inflation without triggering a recession.
Economic Growth vs. Employment Concerns
Interestingly, while inflation remains high, the economy is displaying robust growth, leading some economists to caution against further reductions in borrowing costs. They argue that lowering rates too aggressively could lead to an overheating economy and intensify inflation pressures. Conversely, hiring has significantly slowed since the beginning of 2024, raising concerns regarding the Fed's mandate to maintain maximum employment. Although the unemployment rate remains low at 4.2%, it has increased nearly a full percentage point over the past two years.
Political Landscape Impact
The recent political landscape adds another layer of uncertainty. President-elect Donald Trump has proposed a variety of tax cuts and deregulations which could stimulate economic growth, yet his stance on tariffs and immigration raises concerns about possible inflationary repercussions. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell stated that the impacts of these policies remain unclear until more details emerge.
Future Inflation Projections
Adding to the complexity, the Fed's latest economic projections reflect a slight uptick in expected inflation by 2025, from 2.3% to 2.5%. This potential increase makes it challenging for the Fed to implement further rate cuts, as high interest rates are a primary tool used to combat inflation.
Global Rate Cuts
Globally, it’s worth noting that many central banks are also cutting rates. For instance, the European Central Bank recently lowered its rate for the fourth time in 2023, while the Bank of Canada followed suit with a quarter-point cut last week.
Dissent Within the Fed
In a rare dissent, Cleveland Federal Reserve Bank President Beth Hammack disagreed with the recent decision, advocating for no change in rates, marking the first dissent within the Fed since September.
Consumer Implications
As these developments unfold, consumers are left wondering: How will these interest rate changes affect their financial decisions moving forward? Keep an eye on the implications this could have for the housing market, loan affordability, and overall economic stability in the coming months.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)