Groundbreaking Satellite Technology Unveils Hidden Secrets of Sandy Beaches
2024-12-02
Author: Olivia
Introduction
Scientists have reached a landmark achievement in coastal management with the development of an advanced method to map sandy beach intertidal zones with unmatched precision, using satellite data. This groundbreaking technology allows for accurate measurements of coastlines that are constantly changing due to the relentless forces of tides and waves, delivering essential information crucial for the preservation of these vibrant ecosystems.
The Importance of Sandy Beaches
The research highlights the critical role sandy beaches play as natural barriers—defending coastlines from erosive forces and storm surges while hosting diverse wildlife and recreational activities, including tourism. Traditionally, mapping these coastal areas has proven to be a substantial hurdle, often requiring labor-intensive on-ground surveys that are not only costly but also limited in scope. Rapid changes brought on by storms and seasonal shifts further complicate these efforts, making the need for innovative approaches clear.
Pivotal Research
A team of researchers from Hohai University, in collaboration with international experts, has answered this call in a pivotal study published on November 7, 2024, in the Journal of Remote Sensing. Their cutting-edge methodology hinges on satellite data obtained from the ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 missions, allowing them to create detailed maps of sandy beach intertidal regions.
Methodology
By employing ICESat-2's unique photon-counting lidar technology—which provides high-resolution elevation data—in conjunction with Sentinel-2's optical imagery, the researchers successfully delineated land-water boundaries and developed a comprehensive topographic model. They meticulously processed over 300 cloud-free satellite images captured between 2019 and 2020, resulting in a map with a resolution of just 3 meters and an astounding accuracy of 0.35 meters.
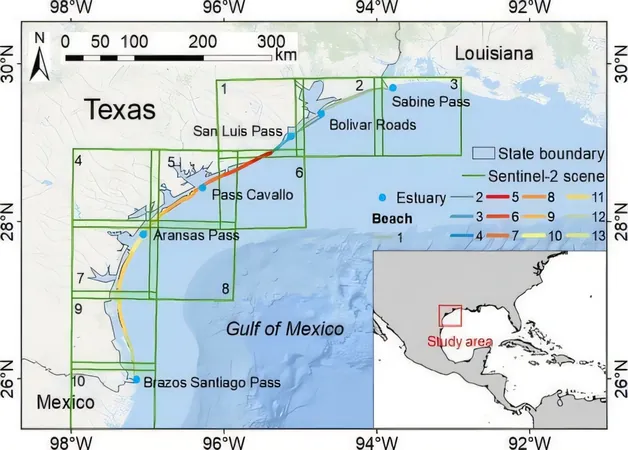
Case Study: Texas Coastline
The implications of this method are vast, as it allows coastal researchers to monitor expansive areas without the need for labor-intensive ground surveys. During their study, the Texas coastline was a focal point, with the team mapping an impressive 38.3 square kilometers of sandy terrain. The analysis revealed critical low-lying areas susceptible to flooding, thus enabling better risk assessments and conservation initiatives.
Expert Commentary
Dr. Lin Wang, the lead researcher of the project, emphasized the importance of this innovation, stating, 'As climate change continues to drive sea-level rise and intensify extreme weather events, this satellite-based mapping tool provides crucial insights for coastal communities globally. By monitoring beaches from a space perspective, we enhance our ability to protect both ecosystems and infrastructure from imminent threats.'
Broader Impact
The advancements in satellite mapping technology go beyond just research implications; they have significant applications in coastal development, disaster response, and ecological conservation strategies. The ability to track beach topography over large distances equips scientists and policymakers to proactively identify erosion hotspots, fortify against storm surges, and analyze the long-term impacts of rising sea levels.
Conclusion
As global coastlines navigate escalating challenges due to climate change, this pioneering technology promises to be a vital resource in fostering resilience and promoting sustainable coastal management practices. Stay tuned as we uncover more about how this innovation could change the future of environmental protection!






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)