Groundbreaking WHO Report Reveals Vaccines Could Slash Antibiotic Use by 2.5 Billion Doses Annually!
2024-10-14
Author: Benjamin
Groundbreaking WHO Report Reveals Vaccines Could Slash Antibiotic Use by 2.5 Billion Doses Annually!
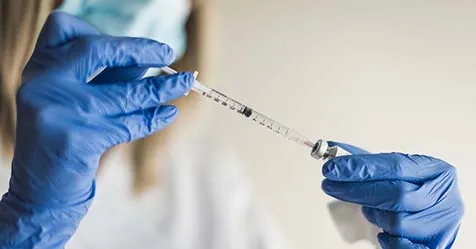
A groundbreaking report from the World Health Organization (WHO) reveals that vaccines targeting 24 different pathogens could significantly reduce antibiotic consumption by up to 22%, equating to a staggering 2.5 billion defined daily doses worldwide each year. This vital finding bolsters global efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR), one of the most pressing public health crises of our time.
AMR occurs when pathogens—such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites—develop resistance to antimicrobial medications, rendering treatments ineffective. The misuse and overuse of these medicines are primary contributors to this growing threat. Shockingly, nearly 5 million deaths each year can be attributed to AMR, highlighting the urgent need for effective preventive measures.
Vaccines are emerging as a crucial weapon in this battle against AMR. Not only do they prevent infections, but they also reduce the dependency on antibiotics, thereby slowing the rise of drug-resistant pathogens. According to the report, existing vaccines for diseases like pneumonia, meningitis, and typhoid could prevent approximately 106,000 deaths linked to AMR annually. Moreover, the introduction of new vaccines for tuberculosis (TB) and Klebsiella pneumoniae could avert an additional 543,000 deaths each year.
"As we seek to address antimicrobial resistance, preventing infections through vaccination is vital," stated Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General. He emphasized that enhancing access to existing vaccines and accelerating the development of new ones will be critical in saving lives and reversing the AMR trend.
Financially, the impact is colossal. The cost associated with treating AMR-related infections is estimated to reach US$730 billion each year. The WHO argues that widespread vaccination could save approximately one-third of these hospital expenses.
Furthermore, during the 79th United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AMR on September 26, world leaders endorsed a political declaration aimed at reducing expected AMR-related human deaths by 10% by 2030. This ambitious plan stresses the importance of vaccines alongside medicines, treatments, and diagnostics, while advocating for new funding and incentives to stimulate research and innovation in AMR solutions.
The timing of this report coincides with International Infection Prevention Week (IIPW) from October 13 to 19, which serves to highlight the critical importance of infection prevention. The week's theme, "Moving the Needle on Infection Prevention," strives to educate communities about the significance of combating misinformation and fostering a new generation of infection prevention practitioners.
With the stakes this high, the message is clear: investing in vaccination, awareness, and innovative research is essential to safeguarding global health and tackling the urgent crisis posed by antimicrobial resistance. Is your community prepared to join the fight against AMR?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)