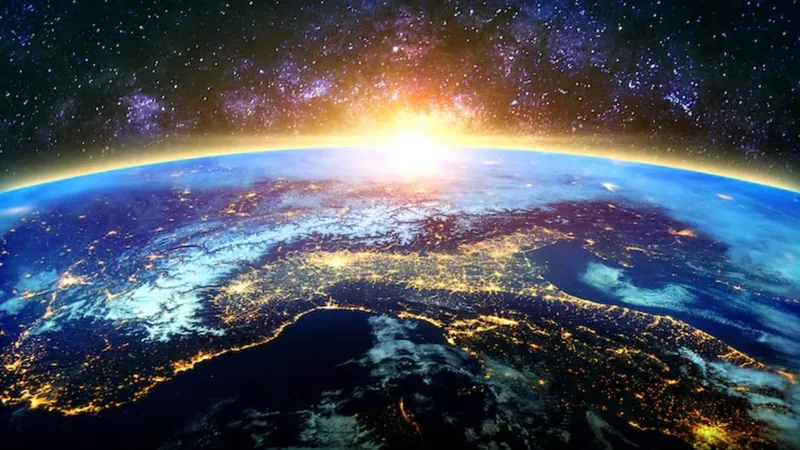

Is Earth’s Magnetic North Pole Racing Toward Russia? A Closer Look at the Alarming Shift
2024-11-20
Author: William
Historical Movement and Recent Acceleration
From the year 1600 to 1990, the magnetic North Pole's movement was relatively slow, averaging about six miles per year. However, from 1990 to 2005, its speed increased dramatically to between 50 and 60 kilometers (31 to 37 miles) annually. A study released in 2020 noted this quickening pace, and if current trends continue, the pole could shift another 660 kilometers (410 miles) toward Siberia within the next decade.
In terms of measurements, the British Geological Survey (BGS) and the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) consistently monitor these changes through a collaborative tool known as the World Magnetic Model (WMM), updated every five years. The latest model has just been released, revealing noteworthy findings about the magnetic field’s behavior.
Why This Matters to Us
You might be thinking, "What does the magnetic North Pole’s movement mean for me?" Surprisingly, it can have widespread impacts on daily life and the global navigation systems we rely on. Magnetic compasses—essential instruments for sailors, pilots, and hikers—depend on the stability of the Earth's magnetic field. Even GPS technology, widely used in smartphones and vehicles, requires updates to accommodate the pole's shifting position.
Dr. Ciaran Beggan of the BGS stated, "In the past 20 years, it accelerated north toward Siberia, increasing every year until about five years ago, when it suddenly decelerated... This behavior we've not observed before complicates our forecasting of magnetic field changes."
The Mystery of the South Pole
While the North Pole is on the move, the South Pole isn't sitting still either; it's shifting eastward along Antarctica's coast. Historically, the Earth's magnetic poles have reversed roughly every 300,000 years, an event that may be overdue based on the last known reversal occurring about 780,000 years ago. This adds another layer of intrigue, as scientists ponder when the next flip might happen.
The Causes Behind the Movement
What drives this magnetic chaos? The swirling molten iron in the Earth's outer core is the source, generating the planet's magnetic field as it moves under the influence of heat. Experts compare these dynamics to "a giant cup of tea"—a hot liquid that constantly churns and influences the magnetic field and the pole's position.
The Consequences of a Weakening Magnetic Field
You may wonder what would happen if the magnetic field were to weaken significantly or disappear entirely. The magnetic field acts as a protective barrier, shielding the Earth from harmful solar radiation. Without it, our planet would face dire consequences: increased radiation levels, a greater probability of mutations in living cells, and heightened cancer risks for both humans and animals.
Additionally, technological infrastructures—including power grids and communication systems—would be severely compromised, leading to potential disruption in daily life, economies, and services.
Final Thoughts
As scientists continue to monitor the magnetic North Pole's rapid movement, it becomes increasingly crucial to understand the broader implications for technology and navigation systems. With these changes affecting everything from air travel to maritime navigation, there's no question: the phenomenon deserves our attention now more than ever. Stay tuned for updates as researchers decode the mysteries behind this unprecedented geological phenomenon!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)