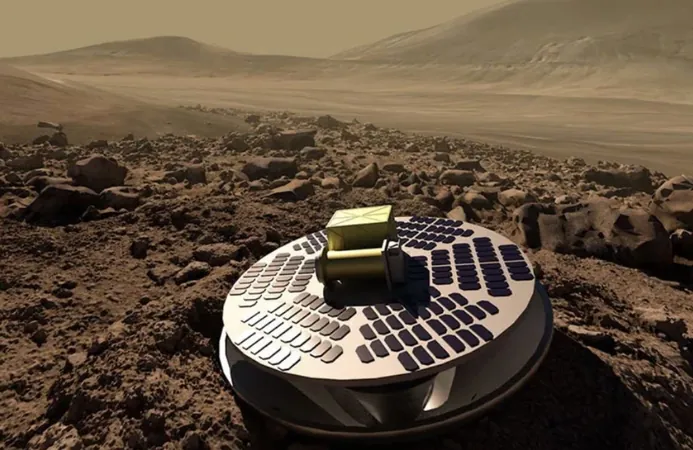

NASA Unveils Bold Vision for Robotic Mars Missions: Are We One Step Closer to Finding Life on the Red Planet?
2024-12-16
Author: Emily
NASA Unveils Bold Vision for Robotic Mars Missions: Are We One Step Closer to Finding Life on the Red Planet?
In a groundbreaking move, NASA has just revealed its refined long-term strategy for robotic exploration of Mars. The space agency is calling for a series of smaller, more frequent missions that will help answer some of the most compelling questions about the planet ahead of any potential human landings.
Overview of NASA's New Strategy
On December 11, NASA unveiled its ambitious plan titled “Expanding the Horizons of Mars Science.” This strategic framework sets the course for the next two decades, emphasizing low-cost missions designed to leverage both commercial and international partnerships. The goal? To maximize exploration opportunities with every available launch window.
According to Eric Ianson, the director of the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters, the final 154-page document builds upon an earlier draft released in March 2023 and includes no major changes. “We initially presented a more succinct PowerPoint package, but this written document outlines our vision in much greater detail,” he explained during a discussion at the annual American Geophysical Union conference.
Significant Components of the Strategy
One of the most significant components of NASA's new strategy is its distinct separation from the ongoing Mars Sample Return program. This separate endeavor is currently under review, with an eye on reducing its cost and schedule. While the recent plan focuses on robotic exploration, it does not currently accommodate any human missions to Mars.
Priority Science Themes
The strategy presents three priority science themes. The first theme revolves around “exploring the potential for Martian life.” Scientists aim to delve into whether life ever emerged on Mars and, if it did, whether it still exists today. The questions are profound: “If life never developed, why not?” The second theme concerns “supporting human exploration,” with a focus on information that robotic missions can gather to inform future crewed missions, thus optimizing astronauts' time and resources on the Martian surface.
Finally, the third theme, “revealing Mars as a dynamic planetary system,” pushes for in-depth study of Mars through comparative planetology. The objective? To understand Mars as thoroughly as we understand our own planet Earth.
A Paradigm Shift in Mars Exploration
NASA is advocating for a paradigm shift in the way we approach robotic missions to Mars. “Every time there’s a launch window, can we send something up?” expressed Ianson. The strategy emphasizes fostering ongoing missions with smaller spacecraft that can deliver findings more rapidly and at a lower cost, estimated between $100 million and $300 million for each mission.
Larger Missions and Advanced Instruments
NASA's vision includes not only these smaller, targeted missions but also larger, more complicated missions that might utilize advanced instruments, like the proposed Mars Life Explorer lander outlined in recent planetary science surveys. Furthermore, the agency plans to utilize “missions of opportunity,” which can involve flying payloads on missions conducted by other space agencies or commercial sectors.
Revitalizing Infrastructure
A key aspect of the strategy involves rejuvenating existing infrastructure on Mars, such as aging communication relays and high-resolution imaging systems provided by the long-operational Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. NASA is looking to the commercial sector for innovative solutions to enhance these capabilities. Earlier this year, the agency contracted nine companies to evaluate the feasibility of commercial systems for delivering payloads and providing vital services.
Challenges Ahead
While this endeavor is promising, Ianson cautions that the viability of commercial missions hinges on a sound business case for these private companies. An ideal model would not simply require NASA to pay for services rendered; instead, there must be some level of upfront investment from NASA to foster effective public-private partnerships.
Initial Steps and Budgetary Considerations
As NASA embarks on this new journey, initial steps are already being taken. The 2025 budget proposal allocates $40 million for advancing Mars robotic exploration technologies, with $30 million dedicated to internal projects and $10 million earmarked for innovative robotics proposals from industry and academia.
Flexible Approach to Mission Planning
While the ambitious plan does not lay out specific mission timelines or budgetary commitments, it embraces a flexible approach, allowing NASA to respond effectively to ever-changing budgetary realities and scientific imperatives. As Ianson put it, “Think of this plan as a menu of options rather than a strict roadmap.”
Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of a new era of Mars exploration, the question on everyone’s mind is: Are we finally on the verge of discovering life beyond Earth? Only time—and these upcoming missions—will tell!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)