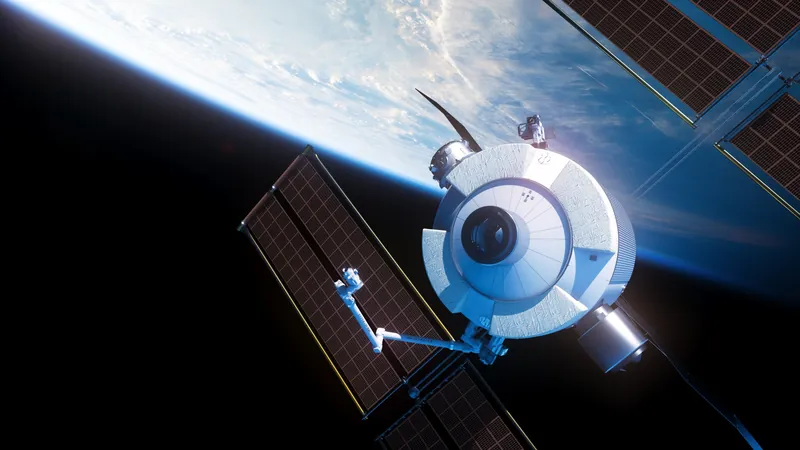

NASA's Starlab: A Leap Towards the Future of Commercial Space Travel
2024-12-17
Author: Michael
Introduction
NASA has announced exciting advancements in the development of Starlab, a commercial space station that's set to redefine humanity's presence in low Earth orbit. Recently, Starlab reached four pivotal developmental milestones that showcase significant progress in its design and operational readiness.
Developmental Milestones
These milestones are part of a collaborative agreement through NASA's Space Act, initiated back in 2021, which emphasizes thorough reviews of essential components such as the preliminary design of the habitat structural test article, systems integration, integrated operations, and a comprehensive habitat structural test plan.
Angela Hart, the program manager for NASA's Commercial Low Earth Orbit Development Program, remarked, "These milestone achievements are great indicators to reflect Starlab's dedication to advancing commercial space destinations. Every successful step brings us closer to a vibrant and robust commercialized low Earth orbit."
Starlab's Design and Features
Starlab is engineered to launch as a fully integrated space station in a single flight, featuring a spacious habitation and laboratory module complemented by a smaller service module responsible for power and propulsion. The ambitious plans for Starlab promise to harness cutting-edge technologies to create an environment where astronauts can live and work for extended periods.
Structural Test Article
Earlier this year, Starlab Space achieved a crucial structural test article preliminary design review, an essential step supported by NASA. This engineering development unit will serve as a basis for testing and verifying the design of the habitation module, which will be astronauts' primary living area aboard the future commercial station.
Test Plan and Integration Operations
Starlab recently unveiled an elaborate test plan that includes an array of qualification tests for the structural test article. These tests range from validating welding processes to rigorous proof pressure and static load testing. Proof pressure tests subject components to significantly higher pressures to confirm structural integrity, while static load tests assess how materials respond to applied loads.
Additionally, important integration operations and systems integration reviews were successfully completed. These reviews provided insights into the station's architecture, segment interfaces, and overall program objectives, establishing a solid foundation for the project moving forward.
Future Plans
Looking ahead, Starlab is on track to finalize a preliminary design review and a phase one safety review by year’s end. This evaluation will ensure the station's design aligns with necessary system requirements, including essential human spaceflight safety standards, while outlining a robust safety approach for the entire project.
Conclusion
NASA is not stopping with Starlab alone; the agency is exploring collaborations on multiple commercial space stations, gearing up to become one of many customers for low Earth orbit services. The ongoing design and development phase will be followed by procurement opportunities with various companies, fostering a sustainable ecosystem for space exploration.
As NASA continues to build on its rich legacy in human spaceflight, the Starlab initiative represents a significant step forward in a new era of microgravity research and commercial endeavors. With the International Space Station nearing its operational twilight, NASA's strategy for low Earth orbit will ensure that the vast benefits of microgravity continue to enrich scientific research and exploration for years to come.
Final Thought
The countdown to a new frontier in space travel is underway—will Starlab be the key to unlocking the next chapter of human exploration?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)