Revolutionary Findings: Lipoxin A4 Could Transform Heart Health in Diabetic Patients!
2024-11-20
Author: Olivia
Recent groundbreaking research reveals that Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) may play a pivotal role in enhancing cardiac remodeling and function in mice suffering from diabetes-associated heart issues. The study focused on the mechanisms through which this molecule can mitigate severe cardiac conditions typically observed in diabetic models.
The Experimental Setup: A Closer Look
In compliance with ethical protocols, scientists used age-matched, six-week-old male ApoE-/- mice to explore the effects of diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction. The team induced type 1 diabetes using streptozotocin (STZ), which significantly increased blood glucose levels and led to the characteristic symptoms of diabetes. Critical metrics like body weight and blood glucose were monitored closely to ascertain the effectiveness of LXA4 treatment compared to control groups.
Innovative Techniques to Assess Cardiac Function
Using advanced echocardiographic techniques, researchers evaluated left ventricular (LV) function to establish the impact of LXA4 treatment. This method enabled them to discern subtle changes in cardiac performance. In addition, the study leveraged histological analyses to assess myocardial fibrosis, inflammatory response, and cellular composition in heart tissues, providing a comprehensive picture of the cardiac pathology involved in diabetes.
The Heart of the Matter: Inflammation and Remodeling
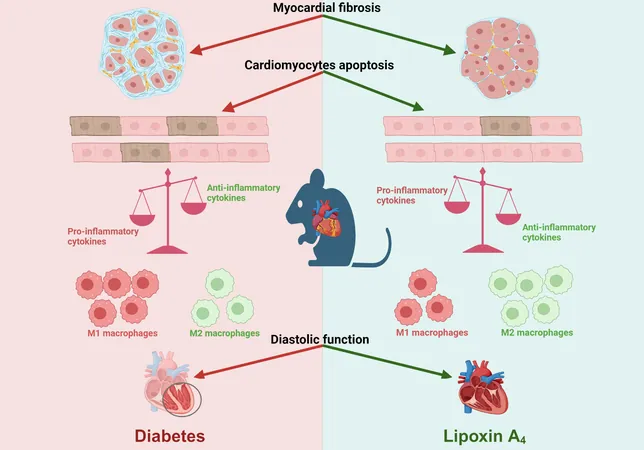
The study highlighted the link between macrophage polarization and the inflammatory response in diabetic hearts. An uptick in pro-inflammatory M1-like macrophages and a decrease in M2-like macrophages indicated a chronic inflammatory state, typical of diabetic conditions. Treatment with LXA4 showed promise in reducing pro-inflammatory markers and promoting a healthier macrophage environment that could aid in tissue healing.
Results indicated a significant decrease in inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, in LXA4-treated diabetic mice. Additionally, LXA4 helped alleviate cardiac fibrosis—a condition characterized by excessive collagen deposition that disrupts normal heart function. This fibrotic process is particularly dangerous in diabetic patients, leading to serious heart complications.
Reversing Cardiac Hypertrophy and Apoptosis
Interestingly, the study found that LXA4 treatment not only reduced cardiac fibrosis but also curtailed cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis—both of which are detrimental outcomes in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Measurements indicated a decline in the cross-sectional area of cardiomyocytes in LXA4-treated animals, underscoring its potential to reverse some diabetic heart pathologies.
Diastolic Function Improvement: A Game Changer
LXA4 treatment also led to improvements in diastolic function in treated mice, indicating that it could confer protective effects on heart health. This is particularly noteworthy as diastolic dysfunction often represents an early sign of heart failure in diabetic patients, making LXA4 a potential target for intervention.
What's Next? Implications and Future Research
While these findings are encouraging, the researchers acknowledge that further studies are warranted to explore the long-term effects of LXA4 and its exact mechanisms in human models. There is also an exciting opportunity to investigate the impacts of LXA4 on ketone body metabolism, especially given its complex interplay with diabetes and heart health.
This study lays the groundwork for novel therapeutic strategies that could transform how clinicians approach diabetic cardiac dysfunction. If LXA4 can be harnessed effectively, it could become a cornerstone in the management of heart diseases associated with diabetes, potentially saving countless lives.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Diabetic Heart Health
The research provides compelling evidence that LXA4 has transformative potential in treating cardiac dysfunction linked to diabetes. As we continue to explore this revolutionary compound's capabilities, the hope is for a future where diabetic heart disease can be effectively managed or even reversed, leading to improved health outcomes for millions affected globally. Stay tuned as the science unfolds!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)