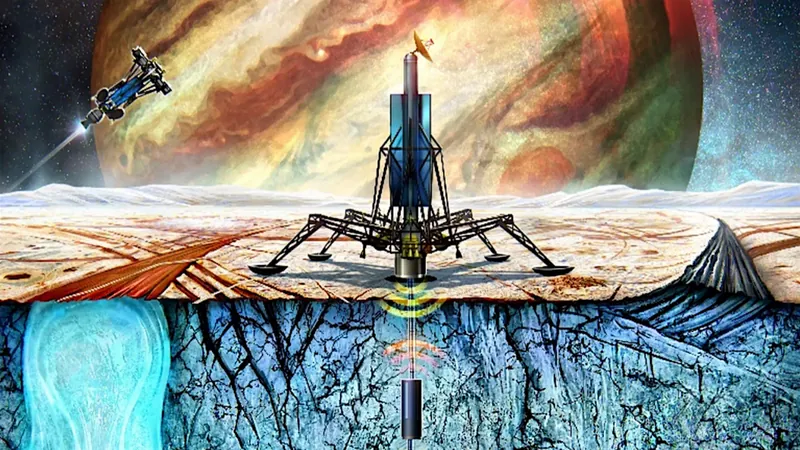

Revolutionary Study Uncovers Travel Times for Probes on Europa's Icy Surface!
2024-11-19
Author: Jacob
Introduction
In an exciting new study, researchers have calculated the travel times for a thermal probe descending through the icy shell of Europa, one of Jupiter's most intriguing moons. The investigation simplifies the complex ice column into a conductive layer, allowing for more precise estimations.
Simulation Methodology
Employing a cellular automaton model, the descent of the probe is simulated by meticulously tracking temperature changes. This innovative approach considers cell interactions dictated by heat conduction, with transitions between cell states determined by their specific temperatures. Validation tests—including a simulation of a soil column and comparisons with experimental data—confirm the reliability and effectiveness of the proposed model.
Results and Findings
The team conducted simulations using two distinct cell sizes, 19 constant probe temperatures, and five variations of ice thermal conductivity. Fascinatingly, the results reveal that smaller cell sizes (Δz = 3 mm) result in significantly shorter travel times. For instance, at a probe temperature of 600 K, the travel time is approximately 22 days, while at a lower temperature of 280 K, it stretches to about four years. In contrast, a larger cell size (Δz = 1 m) leads to much longer travel durations, ranging from an impressive 27 years at 600 K to around 1,000 years at 280 K. Interestingly, the ice shell’s thermal conductivity exerts a modest impact on these descent times, suggesting deeper layers may harbor different thermal behaviors.
Conclusion
The findings are consistent with previous methodologies that engaged more detailed engineering practices concerning probes. This research opens up a thrilling possibility: probes that depend solely on heat production could feasibly traverse Europa's conductive ice shell within the timeframe of a planned mission.
Implications for Future Missions
As missions to explore Europa draw closer, this study elevates our understanding of the moon's icy surface and could play a crucial role in the advancements of astrobiological exploration. For those intrigued by the pursuit of extraterrestrial life, astonishing revelations await as we continue to delve into the mysteries of space!
Stay Informed
Stay tuned for more updates on interplanetary exploration and the groundbreaking technologies that are set to redefine our understanding of the universe!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)