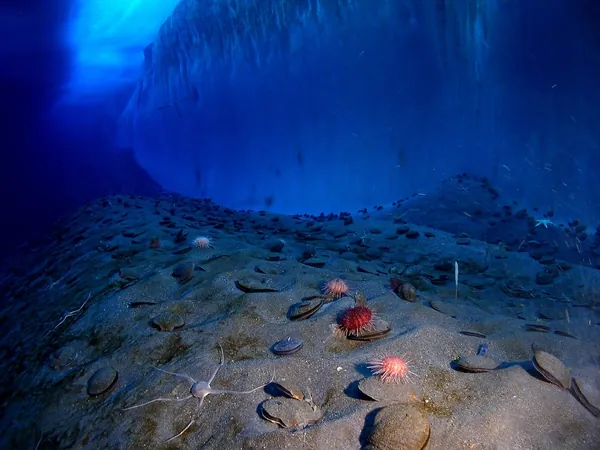

Scientists Unveil Groundbreaking Discovery of 'Dark Oxygen' at the Ocean's Depths!
2025-03-23
Author: Liam
In a stunning revelation that challenges long-held beliefs about oxygen production in our oceans, researchers have discovered a new phenomenon termed "dark oxygen" emerging from the seafloor. This remarkable finding could redefine our understanding of both Earth's deep-sea ecosystems and the potential for life beyond our planet.
The journey began in 2013 when a team of scientists deployed a sophisticated lander system to explore the Clarion-Clipperton Zone in the Pacific Ocean, diving to depths of approximately 4,000 meters. To their astonishment, the system returned with bubbles inside it—an unexpected occurrence that raised immediate questions. Initially skeptical, the scientists returned two years later equipped with oxygen sensors called optodes. However, their investigation led to a startling revelation: rather than measuring oxygen consumption as anticipated, they were documenting oxygen production, effectively turning traditional beliefs on their head.
For years, it was widely accepted that photosynthesis—the process of converting sunlight into energy—was the primary source of oxygen in our atmosphere. However, this new evidence suggested that oxygen can be generated in the complete absence of light. It wasn't until 2021, after employing a secondary measurement technique, that the researchers confirmed they had identified a unique source of "dark oxygen."
Published in the esteemed journal Nature Geoscience in the summer of 2024, the implications of this discovery are monumental. Not only does it open the door to new questions surrounding deep-sea life, but it also prompts a re-evaluation of oxygen production processes in extreme environments, including potential implications for extraterrestrial life on moons like Enceladus and Europa, where sunlight is sparse.
The source of this mysterious dark oxygen is believed to stem from polymetallic nodules—rock-like formations containing metals such as manganese. When these nodules interact with seawater, they may create electrical potential that can split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Recent studies from China lend credibility to this hypothesis by suggesting that oxygen can be generated during the formation of these nodules.
The ongoing quest to explore these groundbreaking findings includes collaborative discussions with specialists at NASA. Scientists are eager to uncover whether the production of dark oxygen is linked to larger microbial communities thriving in the depths of the ocean. The research team is also developing autonomous landers designed to explore uncharted territories beyond 6,000 meters in depth. These innovative vehicles will allow scientists to sample the ocean at depths of up to 11,000 meters, an area that constitutes nearly half of the ocean's expanse and is shrouded in mystery.
As they delve deeper, scientists aim to investigate if hydrogen emerges during dark oxygen production and whether it serves as an energy source for microbial life. Additionally, they will study how climate change may impact these biological activities in the deep sea.
Furthermore, the implications of mining practices for polymetallic nodules in light of the dark oxygen discovery cannot be overstated. These nodules are crucial for producing metals needed in technology like lithium-ion batteries. The need for sustainable practices is paramount, and the outcomes of this research could guide the stewardship of seabed resources and inform regulatory strategies for deep-sea mining.
As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans and the possibilities they hold, one thing remains clear: the spirit of inquiry is alive and well. Scientists are committed to further investigating this astonishing discovery, keeping alive the child-like wonder of asking “Why?” as they unlock the mysteries of our planet and beyond.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)