Shocking New Study Unveils How Aging Brutally Attacks Bone Cells – What You Need to Know!
2025-04-05
Author: Michael
Introduction
As we gracefully move through life, most of us can relate to the feeling that our bodies become a bit creakier with age. But it’s not just our joints that suffer; it turns out our bones are undergoing drastic transformations as well. New groundbreaking research reveals that the cells that form our bones, known as osteocytes, experience significant structural and functional changes over time, which can jeopardize the integrity of our skeletal system.
Groundbreaking Research
A consortium of scientific minds from the University of Texas at Austin, along with experts from Mayo Clinic and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, has made a startling discovery. Their study, recently published in the journals Small and Aging Cell, reveals how aging diminishes the capability of osteocytes to maintain bone strength, contributing significantly to osteoporosis and age-related bone loss.
The Aging Process
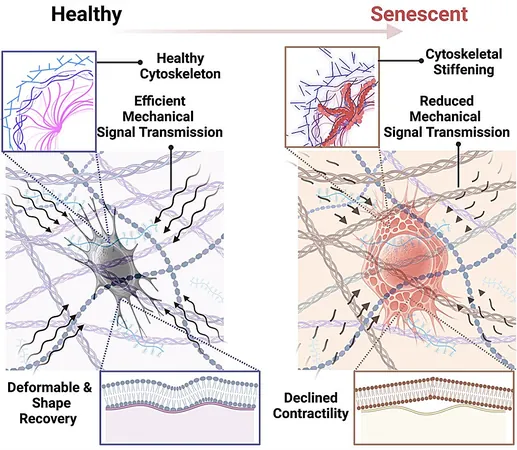
So, what exactly happens when we age? Stressors, both physical and emotional, can lead to a process called cellular senescence. In this state, osteocytes become rigid, undergoing mechanical changes that hinder their ability to detect and respond to the vital mechanical signals required for bone health. This results in disrupted bone remodeling, leading to an increased risk of fragility and fractures.
Role of the Cytoskeleton
Maryam Tilton, an assistant professor at the Cockrell School of Engineering's Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering, states, "Think of the cytoskeleton as the scaffolding inside a building. If that scaffolding becomes inflexible, the structure can’t effectively adapt to changing conditions, leading to potential collapse. Similarly, when osteocytes stiffen, they can’t efficiently manage the ongoing cycle of bone formation and resorption, ultimately resulting in bone loss."
Impact of Senescent Cells
Compounding the issue, senescent cells release a toxic cocktail of substances known as senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), triggering inflammatory responses and damaging neighboring tissues. This has alarming implications, as these cells have been connected to various chronic diseases, including cancer.
Innovative Solutions
Research surrounding cellular senescence has largely focused on genetic markers, which can be inconsistent and difficult to identify across different cell types. However, the research team is shifting the focus toward the physical aspects of cell mechanics. By merging genetic insights with mechanical approaches, they aim to innovate solutions that could transform treatments for aging cells.
Future Directions
Tilton envisions complementing current therapies with biomechanical strategies. "Just as physical therapy can restore movement when our joints become stiff, we're investigating how mechanical cues could reverse or even selectively eliminate these aging cells," she explains.
Promising Alternatives
Dr. James Kirkland, director of the Center for Advanced Gerotherapeutics at Cedars-Sinai and co-leader of the research, adds, "In the near future, biomechanical markers could not only help identify these rogue cells but could also serve as targeted approaches for their elimination, presenting a promising alternative to current drug-based senolytic therapies."
Conclusion
The implications of this research are enormous, especially given the alarming fact that osteoporosis affects millions globally, particularly those over 50. Understanding the mechanisms underlying bone deterioration is essential as the world’s population ages.
Looking ahead, the research team is eager to expand their studies, delving deeper into how various stressors impact osteocytes and what therapeutic interventions may be possible. The quest to keep our bones strong and resilient may be on the brink of a revolutionary breakthrough!
Stay tuned as this exciting field of research unfolds—your bones may thank you for it!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)