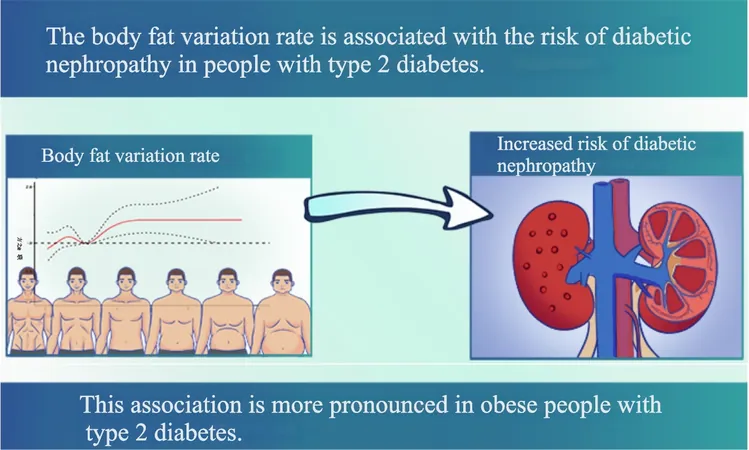
Surprising Link Between Body Fat Fluctuations and Diabetic Nephropathy Risk Revealed in New Study
2024-10-14
Author: Noah
Introduction
Weight management has long been emphasized as a critical strategy in preventing diabetic nephropathy (DN), a serious complication of diabetes. However, recent research has revealed that the fluctuations in body fat during weight management may also play a significant role in increasing the risk of DN among patients with type 2 diabetes. This groundbreaking study, based on data from the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial, sheds light on how body fat variation can complicate an already concerning health issue.
Study Overview
The ACCORD trial followed 10,251 patients with type 2 diabetes over five years. It aimed to evaluate the effects of enhanced control of blood sugar, lipids, and blood pressure on overall health. Participants were carefully monitored for changes in body fat and the development of DN, a condition characterized by kidney damage resulting from diabetes. This posthoc analysis specifically focused on the impact of body fat variation rates (BFVR) on the risk of developing DN.
Key Findings
The study analyzed data from 4,609 participants, observing 1,511 cases of DN. Those with high levels of body fat variation were found to be at a significantly higher risk of developing DN. The statistics were telling: individuals with a higher BFVR had a 13% greater risk of DN compared to those with stable body fat levels. Notably, the association was particularly strong in obese individuals (BMI > 30), where the risk escalated to 34%.
Many of these findings challenged the traditional focus on weight loss alone. Previous research has consistently shown that maintaining a stable weight or minimal fluctuations might be crucial for kidney health. The study suggests that for obese patients, gradual weight loss is advisable to minimize drastic body fat changes that could heighten the risk of kidney complications.
Why Is This Important?
The implications of this research are far-reaching. As diabetes continues to escalate globally, with the World Health Organization predicting that 592 million people will be affected by 2035, understanding the nuances of managing body fat becomes critical. Given that 20-40% of diabetes patients are at risk of developing DN, this new insight could reshape how healthcare providers counsel patients on weight management strategies.
Most importantly, it underscores the need for holistic approaches to diabetes care. Healthcare professionals must not only encourage weight loss but also educate patients on the risks of rapid or excessive fluctuations in body fat.
Conclusion
This study adds a vital piece to the puzzle of diabetes management, particularly for the obese population. It advises a more considered approach to weight loss, encouraging strategies that prevent fluctuations in body fat. As further research explores the optimal ranges for BFVR, patients with type 2 diabetes should be made aware of how their body fat dynamics can influence kidney health.
Call to Action
If you or someone you know is managing type 2 diabetes, consider consulting healthcare professionals about personalized weight management strategies that account for body fat stability. This could be essential in preventing serious complications like diabetic nephropathy. Stay informed and proactive about your health!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)