The Clear Sky Corridor: Revolutionary Insights into Aerosol Formation in Exoplanets Through AI
2024-10-10
Author: William
Introduction
For years, astronomers have faced the daunting task of manually producing accurate transmission spectra for exoplanets, a process both time-consuming and labor-intensive. However, a groundbreaking study showcases an innovative leap forward by harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze light curves and spectroscopic data gathered from transiting exoplanets, specifically using the Hubble Space Telescope’s (HST) Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
AI-Driven Innovations
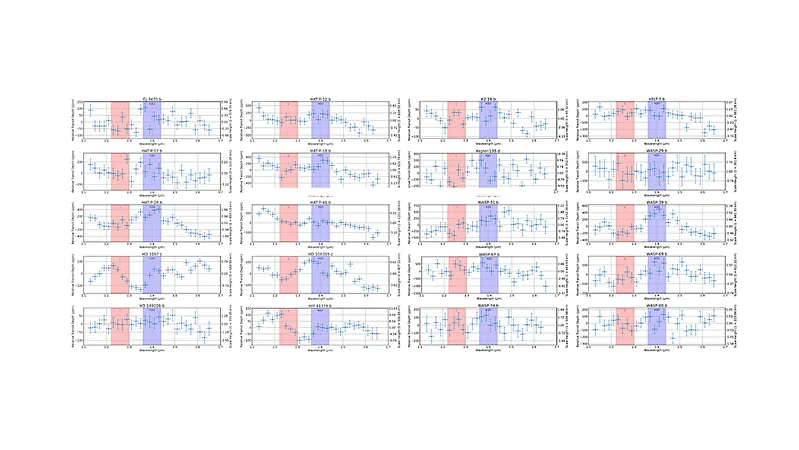
In this phenomenal advancement, researchers have deployed an AI-driven parameter optimizer that operates the Eureka pipeline, enabling the production of standardized transmission spectra from open-access HST WFC3 datasets. This study encompasses a diverse catalog of 43 exoplanets, ranging from scorching hot Jupiters to cooler sub-Neptunes, with temperatures varying from 280 to an astonishing 2580 Kelvin.
Key Findings
One of the most exciting revelations from this research is the confirmed relationship between the water band's amplitude at 1.4 micrometers in hot Jupiters and their equilibrium temperatures. What’s more, a new and intriguing trend has been identified among Neptune/sub-Neptune atmospheres at considerably cooler temperatures.
The Clear Sky Corridor
The study introduces the concept of the "Clear Sky Corridor," a notable diagram that correlates planet mass with equilibrium temperature, indicating that planets falling between 700 and 1700 Kelvin (dependent on mass) experience enhanced H2O band measurements. These findings suggest that metallicity may play a pivotal role in the formation of aerosols in exoplanetary atmospheres.
Implications for Future Research
As the HST lays the groundwork for understanding aerosol formation across various types of exoplanets, this research paves the way for further exploration by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The JWST is set to advance our understanding of these atmospheric trends across a broader spectrum of planets, utilizing its superior imaging capabilities.
Conclusion
This new knowledge not only enhances our comprehension of the atmospheres surrounding distant worlds but also opens up thrilling possibilities for astrobiological research. As scientists equip themselves with AI tools and advanced telescopes, the future of exoplanet exploration promises spectacular developments that could bring us closer to answering profound questions about the universe and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Stay Tuned
Stay tuned for more groundbreaking updates in the realm of exoplanetary studies and learn how these revelations may revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos!






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)