The Stunning Cosmic Dance of R Aquarii: A Celestial Spectacle Unveiled!
2024-11-18
Author: Jacob
Introduction
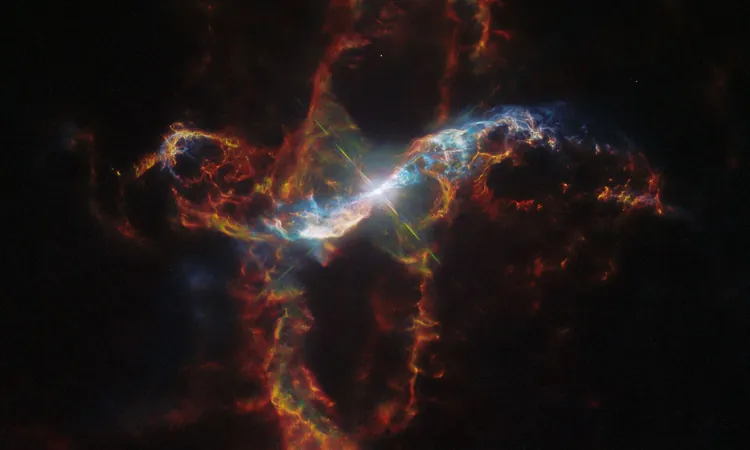
In a mesmerizing display of cosmic artistry, the binary star system R Aquarii, located a staggering 700 light-years away, captivates astronomers and stargazers alike with its chaotically beautiful gaseous filaments. Thanks to the Hubble Space Telescope, we are granted a glimpse into the intricate dance between a white dwarf and a Mira-type variable star, each unique and contributing to this vivid celestial phenomenon.
The Stars of R Aquarii
R Aquarii is characterized by two distinctly contrasting stars. The first, a white dwarf, stands as a remnant of a once vibrant main sequence star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel. This stellar corpse shines with the fading embers of its former self, packing a mass comparable to our sun into a volume similar to that of Earth—creating an incredible gravitational force for its size.
On its cosmic dance floor looms the second partner, a Mira-type variable red giant. This bloated giant is over 400 times the size of the sun and pulsates with life in a fluctuating cycle that spans approximately 390 days, changing its luminosity by a staggering factor of 750. At its peak, this celestial behemoth can shine more than 5,000 times brighter than our own star.
Stellar Interaction and Nova Events
The interaction between these two stars generates breathtaking eruptions every 44 years, sending hydrogen gas shooting outward at breathtaking speeds exceeding 1.6 million kilometers per hour. The white dwarf's powerful gravitational pull siphons hydrogen from the red giant, creating an accumulation that eventually ignites in a cataclysmic explosion. This nova event ejects material into the cosmos, shaping the iconic filaments that make R Aquarii a thrilling sight to behold.
The Role of Magnetic Fields
Even more fascinating is the role of the white dwarf’s intense magnetic fields, which can be millions of times stronger than Earth's. These forces twist the expelled hydrogen gas into intricate streams and spirals, forming a stunning nebula that shines brightly. The glowing gas we observe is ionized hydrogen, whose vibrant colors are augmented by the reddish hue that results from local cosmic dust absorbing blue light.
Timelapse Observations
A recent timelapse series captured by Hubble showcases the dynamic interplay between the stars over the past nine years, revealing the cosmos in a dance of destruction and beauty. However, those mesmerizing gaseous filaments extend an astonishing 400 billion kilometers (248 billion miles) into space—almost 24 times the diameter of our solar system!
Historical Background
R Aquarii's rich history began in 1810 when German astronomer Karl Ludwig Harding first documented it. Since then, esteemed astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, have deepened our understanding of this binary system's complex interactions. The study of R Aquarii is crucial for scientific exploration, shedding light on the mechanics of stellar winds, accretion processes, and the formation of ionized nebulae, offering valuable insights into the lifecycle of stars.
Conclusion
As we continue to unveil the mysteries of R Aquarii, one thing is clear: the cosmos never ceases to amaze us with its extraordinary wonders, urging us to keep looking skyward! Stay tuned for more astonishing discoveries in the heavens above!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)