The Unseen Consequences of the Pandemic: A Deep Dive into US Mortality Trends Through Eight Eye-Opening Charts
2024-12-29
Author: Olivia
The Unseen Consequences of the Pandemic: A Deep Dive into US Mortality Trends Through Eight Eye-Opening Charts
The Covid-19 pandemic, which swept across the globe five years ago, has emerged as one of the worst public health crises in modern history. Its aftermath has left a profound impact on life expectancy in the United States, which plummeted by an alarming 2.7 years during the first two years—marking the sharpest decline since World War II. As we explore this devastating reality, we'll uncover the underlying factors contributing to the rising mortality rates and the broader implications on public health.
1. Heart Disease Worsened by Covid-19
Traditionally the leading cause of death in the United States, heart disease witnessed an exacerbation during the pandemic. The stress and health complications associated with Covid-19 have led to increased cardiovascular issues, pushing more individuals into higher-risk categories.
2. The Stroke Surge
Another alarming trend observed during the pandemic is the surge in strokes, largely attributed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus's ability to cause dangerous blood clotting. These conditions not only claim lives but also lead to long-term disability for many survivors.
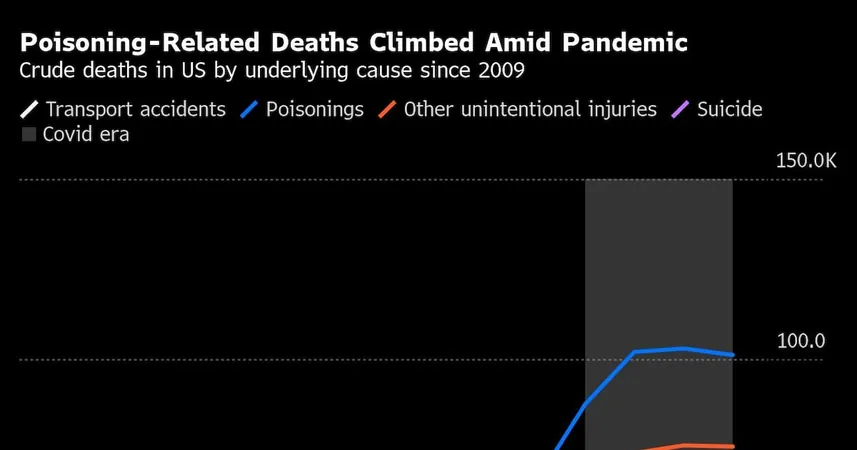
3. The Opioid Epidemic Escalates
The pandemic coincided with a catastrophic rise in opioid-related fatalities. The combination of isolation, economic distress, and disrupted healthcare services resulted in an escalation of overdose deaths, making unintentional injuries the third leading cause of death in the US in 2022.
4. The Alcohol and Liver Disease Compounds
Prolonged lockdowns and increased anxiety have driven many to alcohol for relief, leading to a notable rise in liver disease cases. This trend presents a growing challenge to public health, as liver-related ailments continue to surge.
5. Deaths from Respiratory Illness Declined, Then Spiked
Interestingly, the social distancing measures that followed the pandemic initially led to a significant reduction in deaths from influenza and other respiratory illnesses. However, once these measures were lifted, infections rebounded dramatically, once again posing risks, particularly to vulnerable populations like the elderly and very young.
6. Declining Mortality Rates Amidst Widespread Immunity
As Covid-19 entered its fourth year, a silver lining emerged: widespread immunity through vaccination and prior infections has contributed to a decline in mortality rates. This evolving immunity landscape provides a glimmer of hope in the grappling COVID-19 narrative.
7. Lingering Long-Term Health Effects
Despite some improvement, the long-term health ramifications of Covid-19 continue to surface. Conditions such as increased risk for dementia and neurodevelopmental delays underscore the necessity for ongoing research and attention to those impacted by the virus.
8. The Need for Vigilance Continues
While there's a global urge to move on from the pandemic's turbulent years, it’s crucial to understand that the repercussions of Covid-19—both visible and hidden—remain. As we analyze these trends and foster a more resilient healthcare system, society must remain vigilant to prevent future public health crises.
As we reflect on these grim statistics and the factors at play, it’s evident that the pandemic's shadow looms larger than ever. We must embrace a collective responsibility to ensure that the lessons learned translate into actionable policies and preventive measures to safeguard public health for future generations.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)