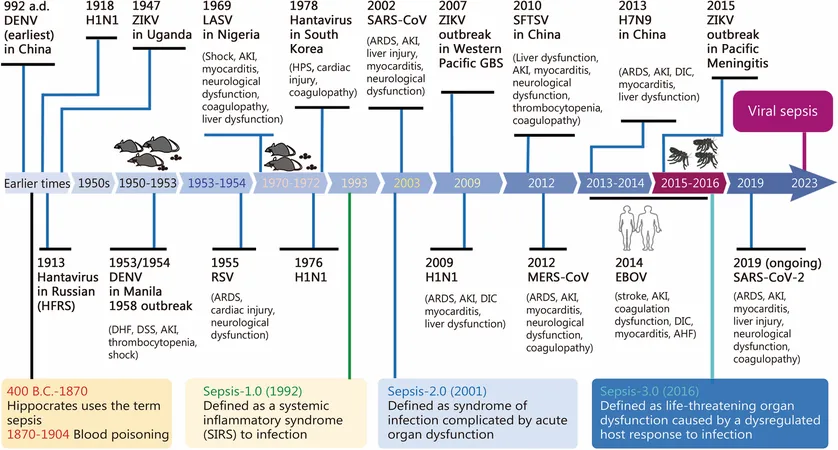
Understanding Viral Sepsis: Insights into Diagnosis, Mechanisms, and Treatment Options
2024-12-16
Author: Jacques
**Title: Understanding Viral Sepsis: Insights into Diagnosis, Mechanisms, and Treatment Options**
Viral sepsis is a critical condition characterized by the body's overwhelming response to viral infections, leading to organ dysfunction and, if untreated, can culminate in severe health outcomes. This condition, while sharing some similarities with bacterial sepsis, has unique complexities and challenges that require careful understanding of its mechanisms and effective treatment options.
### Mechanisms Behind Viral Sepsis
When a virus infects the host, several pathways are activated as a defense mechanism. Notably, pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs), and RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) play a pivotal role in recognizing viral components. This initiate a cascade of signals leading to the secretion of type I interferons (IFNs), crucial for combating viral threats.
However, in viral sepsis, the signaling pathways can be dysfunctional. This dysfunction promotes viral evasion tactics and can worsen tissue damage, making timely diagnosis and intervention vital.
### Viral Immune Evasion Tactics
Certain viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, and others, have evolved to manipulate these immune pathways to enhance their own persistence and replication. These manipulative strategies may include deactivating key adaptors that are necessary for interferon production and enhancing their ability to escape immune surveillance.
### Key Cytokine Pathways and Inflammation
One of the significant contributors to organ dysfunction in viral sepsis is excessive inflammation, often termed a "cytokine storm." This hyperinflammatory state can lead to severe complications like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which has been prominently observed in COVID-19 patients.
Cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α are released in large quantities during viral infections, exacerbating tissue damage and contributing to the manifestations of ARDS. The simultaneous release of histones by dying cells only compounds the effect, further enhancing inflammation and potentially leading to multi-organ failure.
### Cellular Stress and Metabolic Dysregulation
Viral infections can lead to cellular stress responses and metabolic disorders, including endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. These disruptions can worsen inflammation and organ damage, creating a vicious cycle that may result in outcomes like ARDS, cardiac complications, and even long-lasting sequelae in survivors.
For example, during COVID-19, patients often experience significant mitochondrial dysfunction due to the metabolic footprint left by viral replication, which is coupled with increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
### Treatment Approaches to Viral Sepsis
Treating viral sepsis poses unique challenges, primarily due to the lack of effective antiviral agents compared to bacterial sepsis treatments. Nonetheless, several therapeutic strategies are either in practice or being explored:
1. **Supportive Care**: This includes fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and respiratory support, such as mechanical ventilation, to stabilize patients. The recent advances in technologies like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation have shown promise in improving outcomes for severely ill patients.
2. **Direct Antiviral Strategies**: Various antiviral drugs target specific stages of viral replication. Remdesivir, for instance, has been shown to be effective against SARS-CoV-2, significantly leading to reduced hospitalization rates.
3. **Immunomodulatory Therapies**: Approaches such as cytokine antagonists can help to mitigate harmful inflammatory responses without suppressing protective immune functions. Targeting IL-6, for example, has shown promise in reducing mortality rates among severe COVID-19 cases.
4. **Convalescent Plasma Therapy**: The transfusion of plasma from recovered individuals has shown potential in providing immediate antibodies for passive immunity. This approach has been notably effective in early viral outbreaks.
5. **Cellular Therapies**: Advanced therapeutic modalities like NK cell and T cell therapies are being explored to enhance the body's ability to combat viral infections without inducing excessive inflammation.
### The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early recognition of viral sepsis is paramount. Understanding the underlying mechanisms can guide timely interventions, which are crucial in preventing irreversible damage. As research progresses, an integrated approach combining supportive care, targeted antiviral therapies, and immunomodulation will likely pave the way for better outcomes in patients afflicted by viral sepsis.
In conclusion, viral sepsis represents a formidable challenge in clinical medicine with significant implications for patient care. While treatment effectiveness continues to evolve, maintaining a focus on both immediate management and long-term recovery strategies will remain essential in combating this serious condition.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)