Unlock the Secrets of Your Gut: A Revolutionary Map to Personalize Your Diet!
2024-10-04
Understanding Gut Health
In the world of health and wellness, "gut health" has become a sensational buzzword capturing the attention of food enthusiasts and dietitians alike, and for a compelling reason. A staggering array of trillions of microbes and bacteria inhabiting our gut play critical roles in our overall health and susceptibility to various diseases.
Groundbreaking Research from Yale University
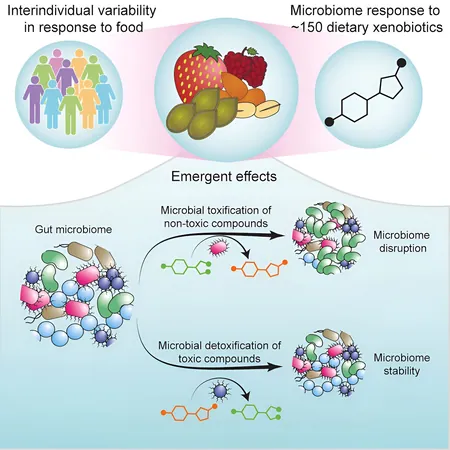
Recently, a groundbreaking study from Yale University's Microbial Sciences Institute has illuminated the path towards a revolutionary approach to personalized nutrition, catering to the unique needs of our gut health. Led by the esteemed Andrew Goodman, this research produced the first comprehensive molecular map showcasing the intricate interactions between food molecules and our distinct gut bacteria. Their remarkable findings were published in the prestigious journal Cell.
The Mystery of Dietary Responses
Building upon previous studies that explored the connection between medicinal drugs and gut microbiomes, the researchers sought to unravel the enigma of why individuals often react differently to identical foods. Elizabeth Culp, a key contributor to the study and former postdoctoral fellow in Goodman's lab, shed light on this phenomenon, stating, "Diet plays a monumental role in our health and profoundly influences our microbiome."
Beyond Macronutrients: The Importance of Small Molecule Components
While considerable research has focused on the impact of macronutrients like fiber on our gut bacteria, the spotlight has been dim on the small molecule components within our food that may drive health issues. Culp explains, "There is a lack of empirical evidence guiding dietary adjustments for managing disease risk factors such as diabetes or cancer, possibly due to the unique ways our microbiomes respond to identical food molecules."
Creating a Systematic Map of Food-Microbe Interactions
To address this, the research team created a systematic map detailing the interactions between small food molecules and various gut bacteria. This groundbreaking work is among the first to clearly outline the specific microbial genes that are responsible for the metabolic alteration of dietary components, as well as the mechanisms through which these components influence our microbiomes.
Experimental Techniques and Findings
Utilizing advanced liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry techniques at the Yale West Campus Analytical Core, the scientists experimented with approximately 150 dietary "xenobiotic" compounds. Coupled with genome sequencing from the Yale Center for Genome Analysis, they assessed how these compounds impacted the composition of human gut microbial communities.
Variability in Individual Responses
Surprisingly, Goodman observed a significant level of variability in responses: "The same dietary compound could dramatically reshape certain individuals' gut microbial communities while having little to no effect on others." This newly devised molecular map provides groundbreaking insight into the varying responses of individuals to dietary compounds, shedding light on how these compounds stimulate the growth of beneficial or harmful gut bacteria.
Implications for Personalized Nutrition
While predicting how a person might respond to a particular food—and the ultimate impact on their health—remains a complex challenge, these findings lay the groundwork for comprehending the metabolic variations among individuals. Understanding these differences could provide essential insights into combating fate-determining diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and gastrointestinal infections.
Future Directions in Gut Health Research
Culp, now a scientist at Empress Therapeutics in Boston, emphasizes the long-term potential of their research: "If we can pinpoint the specific microbial genes that dictate a microbiome’s response to food molecules, correlations to diseases can begin to make sense." This innovative study marks a significant milestone in the journey toward personalized dietary recommendations that cater to individual health needs. Your health journey might just get personalized like never before!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)