
Unlocking the Secrets of Our Immune System: How a Genetic 'Tuning Dial' Could Explain COVID Severity Differences!
2024-12-12
Author: Noah
Introduction
Why does COVID-19 affect some individuals more severely than others? For years, researchers have been focused on the interferon pathway—an essential component of our immune response. When our cells detect an infection, they produce a protein called interferon, which alerts surrounding cells to combat the virus.
However, when this signaling process malfunctions—either overreacting or underreacting—it can lead to serious health issues, including severe COVID-19 symptoms or long COVID. Disruptions in this pathway have also been linked to autoimmune diseases and various forms of cancer, yet the underlying causes of these immune system errors remain largely unexplored.
Ground-breaking Study
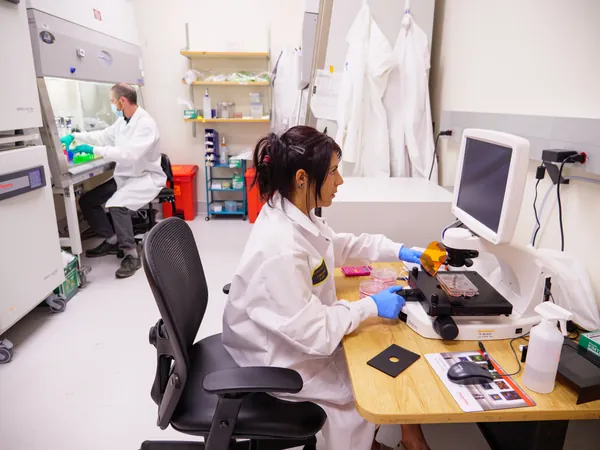
A ground-breaking study from CU Boulder has recently shed light on this mysterious phenomenon. Published in the journal Cell, the research identifies what the authors refer to as an "immune system tuning dial," a genetic alteration that emerged millions of years ago. This discovery could have significant implications for understanding immune responses and developing new treatments.
Senior author Ed Chuong, an assistant professor at the BioFrontiers Institute, highlights the importance of an overlooked category of protein variants that can significantly influence immune function. The study revealed that a specific variant of a protein called IFNAR2 seems to act like a tuning dial, enabling researchers to potentially manipulate immune system activity. “If we can adjust this dial, it could lead to innovative therapies for infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers,” said Chuong.
How Evolution Gave Us a 'Bug' That Helps Fight Disease
The research delves into the role of transposons—genetic elements that have embedded themselves in primate genomes over the last 70 million years. Some of these, known as endogenous retroviruses, have evolved to support cancer cell survival; others, however, have effects that researchers are only beginning to understand. Team member Giulia Pasquesi explained the significance of these transposons: “Think of them like unexpected words appearing in a sentence that can alter the meaning of a gene.”
Most often regarded as 'junk DNA,' these genetic hitchhikers may hold the key to significant immune functions. Upon analyzing cutting-edge genetic sequencing from human tissues, Pasquesi pinpointed 125 genetic variants linked to immune functionality.
The pair zeroed in on the variant of the IFNAR2 protein, which is crucial for transmitting interferon signals that help fight off infections and diseases like cancer. Their findings revealed that the newly identified 'short' variant of IFNAR2 acts as a decoy, interfering with normal signaling, and was present in all human cells.
Further laboratory experiments demonstrated that removing this short variant heightened cellular sensitivity to interferon. In essence, cells without the decoy variant exhibited stronger immune responses against viruses, including SARS-CoV-2—the virus responsible for COVID-19—and dengue virus.
Conclusion
This research indicates that the balance between different IFNAR2 variants serves as a 'tuning dial' that controls immune strength, varying from person to person. Those with higher quantities of this variant may face a greater risk of severe infections, while others might deal with chronic issues like inflammation or autoimmune diseases.
“We've unveiled a new control mechanism that may explain the diversity of immune responses seen among individuals,” said Chuong. The team has already initiated efforts to patent their discovery and test therapeutic compounds aimed at this genetic dial.
This study is a milestone, suggesting that the IFNAR2 protein's story could represent just the beginning of uncovering countless immune regulatory functions hidden within our DNA. "Exploring the less understood areas of our genome is crucial for unlocking new breakthroughs that can enhance human health," Chuong concluded.
As research continues, it opens a world of possibilities, potentially revolutionizing our approach to treating infections and immune-related disorders, and further raising awareness about the complexities of our immune systems. Stay tuned for more groundbreaking discoveries on how the hidden intricacies of our genetics can shape our health outcomes!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)