
Unmasking Anomalies: How Undercomplete Autoencoders Are Revolutionizing Rover Mobility Monitoring on Mars
2024-12-02
Author: William
Introduction
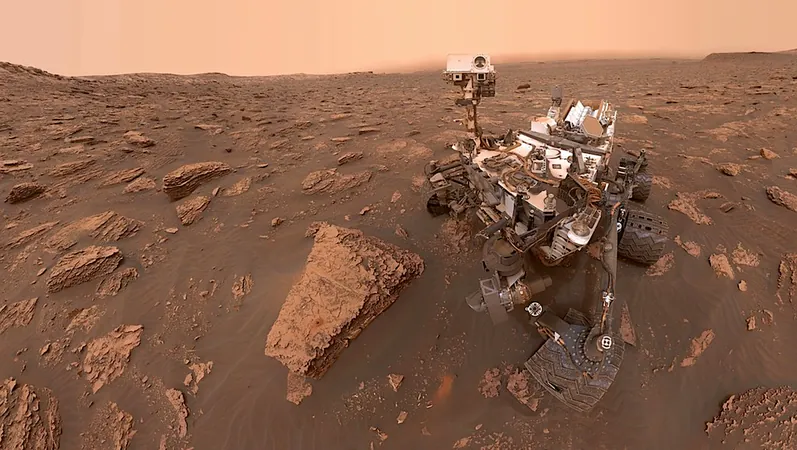
Eleven years into its groundbreaking mission, the Mars Science Laboratory continues to play a crucial role in NASA's exploration of the Red Planet. Ensuring the long-term functionality of the Curiosity rover remains a top priority, especially as it faces the harsh Martian environment.
Innovative Approach
Recent research introduces an innovative approach using undercomplete autoencoders to detect drive anomalies in the rover. By utilizing telemetry data from wheel actuators, the Rover Inertial Measurement Unit (RIMU), and the suspension system, scientists are enhancing their ability to analyze rover performance during critical downlink sessions.
Model Evaluation
The study meticulously examines various model architectures and input features, evaluating how these factors influence the performance of the anomaly detection systems. By testing these models on previously unseen data, researchers aim to create scenarios that closely mirror real-world conditions faced by the rover.
Results
The results are impressive: the undercomplete autoencoder model not only identifies drive anomalies effectively, but it also uncovers subtle telemetry patterns that human operators may overlook. This advanced detection capability is crucial, as it can signal the onset of potential failures, allowing for timely interventions.
Insights and Implications
Furthermore, this research provides valuable insights into the best practices for model design, aiding in the optimization of future rover missions. The implications for planetary exploration are significant; improved reliability and early anomaly detection could be the key to safer and more successful missions in the cosmos.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of undercomplete autoencoders in monitoring rover mobility is a game-changer. As scientists continue to refine these models, the prospect of safeguarding robotic explorers against unpredictable challenges becomes increasingly bright. The success of this technology could pave the way for future innovations in space exploration, ensuring that humanity's quest for knowledge continues unabated.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)