Unraveling the Secrets of the cpb2 Gene: A Game-Changer in Combatting Clostridium perfringens Infections
2024-10-14
Author: Amelia
Introduction
Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens) is notorious in the microbiological world, lurking in the intestines of both humans and animals while being responsible for a range of severe enteric diseases. This bacterium is infamous for its production of more than 20 toxins; among them, the β-2 toxin (CPB2) has garnered particular attention due to its strong association with intestinal infections.
Initially identified in piglets suffering from necrotizing enterocolitis, CPB2 has now been documented in various species. Surprisingly, the genetic aspects and host adaptations linked to this toxin remain insufficiently explored, prompting urgent calls for research into the cpb2 gene's role in the evolution of this pathogen.
Research Findings
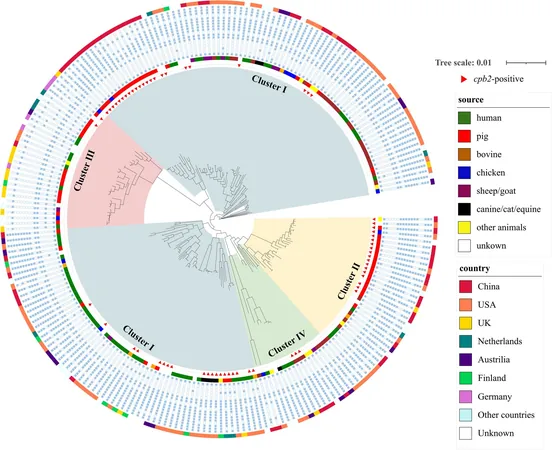
A groundbreaking study from scientists at Northwest A&F University, published on August 30, 2024, in the journal *One Health Advances*, sought to shed light on the genomic framework of C. perfringens strains that possess the cpb2 gene. Researchers set their sights on the potential biological significance of the gene, as well as its association with specific host species.
Analyzing a staggering 763 genomes of C. perfringens from various hosts, researchers found a striking prevalence of the cpb2 gene among strains derived from pigs. While the presence of cpb2 appears to be a significant feature in pig strains, its influence on the evolutionary trajectories of bacterial strains was found to be minimal. Instead, the cpb2 gene was situated within a conserved genetic region on plasmids, hinting at opportunities for horizontal gene transfer among different strains.
Key Insights
A particularly fascinating aspect of this research was the gene's consistent linkage with a transcriptional regulator, suggesting that this may be key to its survival and persistent presence in select hosts. Additionally, the study indicated that the cpb2 gene is intricately related to adaptations tailored to specific species, particularly within the porcine gut. This revelation strongly suggests that C. perfringens optimize its survival strategies by leveraging this gene, though its precise role in other host species remains a mystery.
Expert Commentary
Dr. Juan Wang, the lead investigator of the study, articulated the significance of their findings: "Our research offers an in-depth genomic analysis of the cpb2 gene, underscoring its critical role in host adaptation among pig-derived strains. Gaining a clearer understanding of its functionalities could lead to innovative strategies to mitigate C. perfringens infections, especially within the livestock sector."
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of this study are tremendous, resonating not just within the scientific community but also in public health and animal husbandry. C. perfringens poses significant risks to livestock, particularly pigs; therefore, deciphering the genetic mechanisms that underpin its adaptations could pave the way for novel intervention strategies. Moreover, these insights may serve to target and prevent C. perfringens-associated diseases in both animal populations and human health, highlighting the urgency of this research in safeguarding the wellbeing of our livestock and, ultimately, our communities.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as scientists continue to explore the enigmatic world of bacteria, armed with new tools and technologies to unveil the mysteries behind some of our most challenging pathogens. Is this the breakthrough we've been waiting for? Only time will tell!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)