
Unveiling the Devastating Reality: Human-Caused Bird Extinctions Have Over 3 Billion Years of Evolutionary History at Stake!
2024-10-03
Introduction
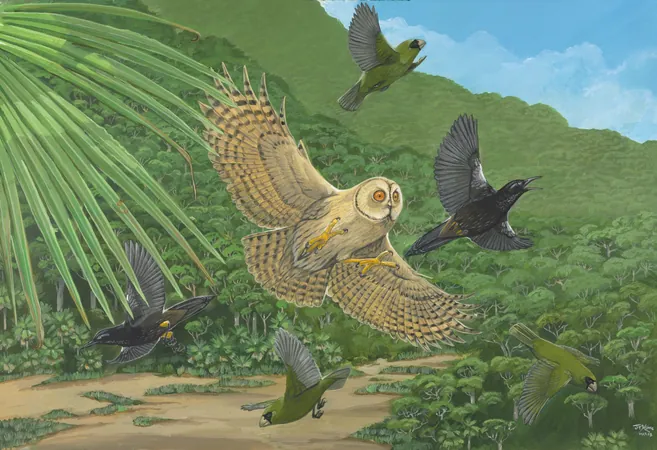
A groundbreaking study reveals a stark reality: the extinction of numerous bird species due to human activities over the past 130,000 years has severely diminished avian functional diversity—the various roles birds play in ecosystems. This alarming trend has led to the loss of nearly 3 billion years of distinct evolutionary history, according to research published in the prestigious journal Science.
Human Impact on Bird Extinction
While it's widely recognized that human actions have driven a global decline in species richness, the effects of past extinctions on other aspects of biodiversity remain underexplored. Researchers from the University of Birmingham emphasize the dire implications of the ongoing biodiversity crisis and the critical need to understand which ecological functions are deteriorating as species vanish.
Historical Context of Extinctions
From the famously extinct Dodo to the recent disappearance of the Kaua‘i ‘Ō‘ō songbird earlier in 2023, current evidence indicates that at least 600 bird species have been lost due to human activity since the Late Pleistocene, when modern humans began their global expansion.
Research Findings
The research team utilized the largest and most comprehensive dataset on bird extinctions from the Late Pleistocene and Holocene epochs. The pivotal study titled "The Global Loss of Avian Functional and Phylogenetic Diversity from Anthropogenic Extinctions" delves into not just the sheer numbers of extinctions but also the broader consequences for planetary health.
Importance of Each Species
Lead author Dr. Tom Matthews from the University of Birmingham underscores the significance of each bird species, saying, "Extinctions are not just about counting numbers; every species contributes to its environment and holds an essential role within its ecosystem."
Ecological Roles of Birds
Birds provide critical services such as pest control by consuming insects, recycling nutrients through scavenging, seed dispersal, and pollination. The extinction of these species means the eradication of their important ecological functions.
Consequences of Avian Diversity Loss
The findings indicate that human-induced bird extinctions have resulted in the loss of approximately 3 billion years of unique evolutionary history and a shocking 7% of global avian functional diversity. This figure greatly exceeds expectations based solely on the number of extinctions documented.
Implications for Ecosystems
This loss of avian diversity has far-reaching consequences, including diminished pollination for flowers, reduced seed dispersal, and weakened natural control over insect populations, thereby increasing the threat of pests and diseases. Additionally, the reduction in scavenger birds could lead to more disease outbreaks due to less carrion being consumed.
Impact on Plant Species and Climate Adaptation
Moreover, this decline in global bird species will likely hinder the capability of numerous plant species to adapt to the changing climate—an ongoing issue critical for biodiversity resilience.
Call to Action
Dr. Matthews warns, "These results serve as a significant reminder that the current extinction crisis involves more than just the number of species. Understanding the declines in avian functional and phylogenetic diversity driven by human activities is crucial."
Future Projections and Conservation Needs
As projections indicate that up to 1,000 additional bird species may face extinction in the coming two centuries, this research highlights the urgent need for effective global conservation strategies, as well as ecosystem restoration and rewilding initiatives. The time to act is now—we must comprehend the ongoing losses in biodiversity to mitigate future devastation.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)