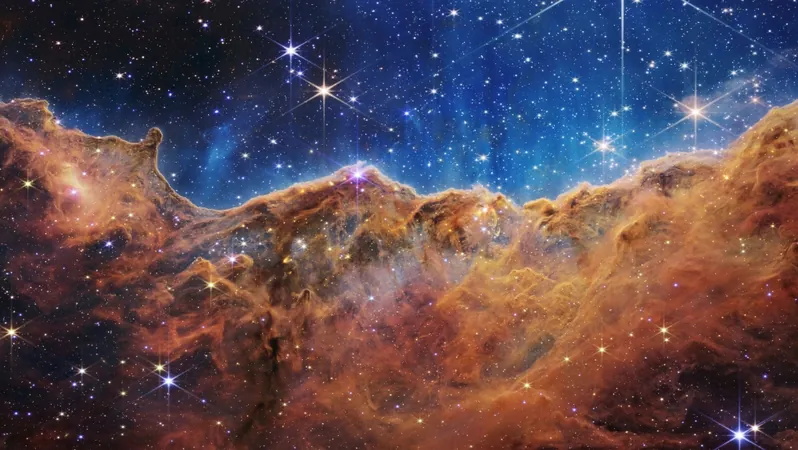

Webb Telescope Unveils Shocking Truth: The Universe is Expanding Faster Than Ever!
2024-12-09
Author: Amelia
In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists have confirmed using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope that our universe is expanding at a rate that defies previous expectations. This astonishing finding has reignited debates around the perplexing notions of dark energy and dark matter, the enigmatic cosmic components that constitute about 96% of everything in existence.
After analyzing two years' worth of data from the Webb telescope, researchers have established that the universe's expansion is significantly outpacing the predictions grounded in centuries of astrophysical knowledge. Specifically, the rate is nearly 8% faster than what models based on our understanding of cosmic evolution would suggest—a phenomenon known as the Hubble Tension.
Lead author of the study and esteemed astrophysicist, Adam Riess from Johns Hopkins University, emphasized the importance of this data: "This is the most comprehensive sample from the Webb Telescope, and it validates the perplexing findings of the Hubble Space Telescope—our universe's growth surpasses the predictions of our best theoretical models." He argues that this points to a gap in our understanding of the universe, particularly regarding dark matter and dark energy.
To clarify, dark matter makes up an estimated 27% of the universe and eludes direct detection. It's understood primarily through its gravitational influence on visible matter—like stars and galaxies. Meanwhile, dark energy, which is thought to account for around 69%, acts as a mysterious repulsive force driving the universe's continued acceleration.
What could possibly explain this unexpected expansion? Riess suggests an array of hypotheses, including revisions to our current models of the universe, potential gravitational anomalies, or even exotic forms of dark matter and dark energy that haven't been fully explored yet. Future research could delve into additional components like neutrinos—subatomic particles that rarely interact with normal matter but are crucial to our understanding of cosmic behavior.
The scientists employed various methods to quantify this cosmic expansion, analyzing distances from Earth to galaxies populated by pulsating stars known as Cepheids. These measurements revealed a consistent harmony between the Webb and Hubble data, highlighting an intriguing pattern and reinforcing the findings.
While the typical value for the Hubble constant—the rate of expansion—should hover around 67-68 kilometers per second per megaparsec, the Webb observations suggest a much higher average of about 73, heightening the tension surrounding this cosmic riddle.
This alarming revelation continues to build on the legacy of the Big Bang, which marked the universe's inception approximately 13-14 billion years ago. Despite the standard model of cosmology suggesting a gradual and predictable expansion, recent developments indicate a far more complex narrative.
As astronomers eagerly pursue further data, they hope to pinpoint the extent and implications of this discrepancy. Questions remain: How significant is the gap in our measurements? Is this mismatch a minor aberration or something truly monumental? Only time and further exploration will unveil the secrets lurking in the cosmos.
In essence, the Webb Telescope isn't just affirming existing beliefs; it’s challenging scientists to reevaluate everything we think we know about our universe. Buckle up, because our understanding of the cosmos is on the brink of a revolutionary transformation! Stay tuned as we continue to unravel this cosmic mystery!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)