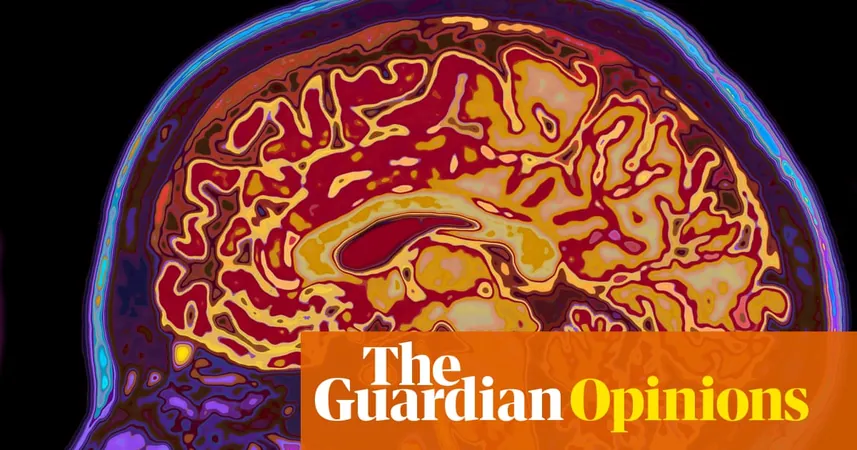

Will We Face a 'Dementia Tsunami'? The Surprising Truth Revealed!
2025-04-08
Author: Emily
Introduction
Amidst alarming forecasts of a looming "dementia tsunami," it’s vital to dissect the deeper truths about dementia's impact on our aging population. In the UK, Alzheimer's disease and related dementias topped the charts as the leading cause of death in 2021, surpassing even Covid-19 and heart disease. In the U.S., it ranks among the top ten causes of death. Dementia is a blanket term that encompasses various diseases that progressively damage brain cells, impairing memory, thinking skills, and overall cognitive function. This harrowing condition affects not only those diagnosed but also their families, as loved ones witness the painful decline of recognition and independence.
Statistics and Predictions
Recent global research paints a concerning picture for future dementia rates. A pivotal study published in *Nature Medicine* examined 15,000 middle-aged Americans and estimated that a staggering 42% of individuals aged 55 and older will develop dementia at some point in their lives — a statistic that has significantly risen in recent years. With projections indicating that the annual count of new dementia cases in the U.S. could double over the next 40 years, public health officials are understandably alarmed.
Emerging Data
However, this dire narrative is currently being challenged by emerging data that suggests a decline in age-specific dementia rates. Research spanning several countries, including Sweden, the Netherlands, and the UK, shows a decline of approximately two-thirds in dementia rates from 1984 to 2024. This indicates that while the older population is growing, the likelihood of developing dementia at specific ages is decreasing. In layman's terms, we are witnessing fewer cases of dementia per age group, suggesting an improvement in longevity and cognitive resilience.
Factors Contributing to Decline
The reasons behind this striking decline in dementia rates remain a topic of extensive research, with several hypotheses being suggested. Factors such as decreased smoking rates, higher levels of education, better management of health conditions like hypertension, and improved early detection of cognitive issues may all contribute. The Lancet Commission has identified that roughly 45% of dementia cases could be avoided by addressing 14 modifiable risk factors, including poor education, lack of exercise, smoking, and social isolation. This points to significant opportunities for both individual and community intervention in preventing the onset of dementia.
Advancements in Treatment
Moreover, significant strides in medical research are paving the way for innovative treatments. Recently, two new drugs — donanemab and lecanemab — have shown promise in slowing Alzheimer’s progression. Pharmaceutical companies have optimistically announced that these breakthroughs may signal the start of a major turning point in Alzheimer’s treatment, although we must remain cautious regarding the high costs and potential side effects associated with these therapies.
Contrasting Trends in Cancer Rates
In contrast to the waning dementia rates, the future of cancer prediction looks grim. Young people today are at a higher risk of certain cancers than previous generations, a phenomenon termed the "birth cohort effect." For example, diagnoses of colorectal cancer have surged by 70% among 15-39-year-olds in G20 countries from 1990 to 2019, highlighting a disturbing trend in cancer incidence.
Conclusion
Ultimately, while we all must confront mortality, the key public health objective is to postpone illnesses like dementia and promote healthier, longer lives. Although concerns about a "dementia tsunami" persist, recent findings offer a glimmer of hope — progress is underway in both public health initiatives and medical advancements aimed at delaying the onset of cognitive decline. The message is clear: with proactive measures, we can ensure that the fight against dementia is both informed by evidence and driven by hope.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)