Australian Researchers Create Nano-Scale Dinosaur Using DNA Building Blocks – Discover the Future of Nanotechnology!
2024-11-27
Author: Yan
Introduction
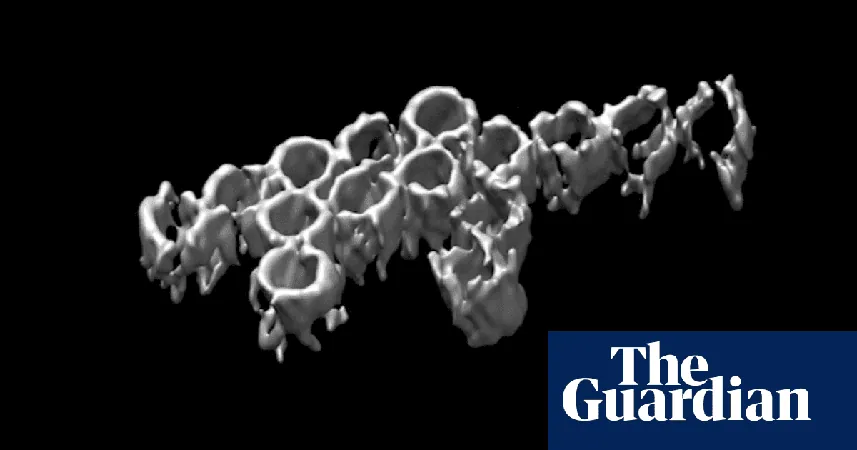
Exciting news from the world of science: researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have achieved a groundbreaking feat by creating a variety of nano-scale structures using DNA as their primary building material. Among their impressive creations is an incredibly tiny dinosaur, just a fraction of the size of a human hair! This innovative approach could revolutionize the realm of nanobot technology.
Research Overview
Published in the prestigious journal Science Robotics, the research highlights the transformative potential of DNA not only as genetic information but as a modular material for constructing complex nanostructures. In total, the team produced over 50 different shapes during their experiments, ranging from dragons and dinosaurs to a magnificently detailed micro-map of Australia, measuring a mere 150 nanometers wide.
Expressing Enthusiasm
Dr. Shelley Wickham, the lead scientist of the team, expressed her enthusiasm for the dinosaur model, noting that its intricate design featured both flexible and compact parts, making it a perfect illustration of their advanced techniques. “This wasn’t something that could come together by chance; it required precise engineering,” she remarked.
Paradigm Shift in DNA Application
Professor Arnan Mitchell, director of RMIT’s micro-nano research facility, emphasized that the approach views DNA as a mechanical object rather than merely a chemical one. This paradigm shift opens up exciting possibilities in fields like targeted drug delivery. By enveloping drugs in DNA structures, researchers can enhance the precision of treatments—delivering medication exactly where it's needed while using external stimuli like light or heat to release the drug.
Future Vision
Looking ahead, Wickham shares her vision of a future where nanobots, built using these techniques, could perform a myriad of tasks—from targeted therapies in medicine to the assembly of cutting-edge electronic devices. The ability to control and manipulate these nano-scale workers may be key to unlocking new technologies.
Creation of Voxels
The process of creating these innovative building blocks, referred to as “voxels,” involves extracting DNA from bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and utilizing a method known as DNA origami to form shapes. These voxels self-assemble through carefully sequenced DNA strands that act like Velcro, binding together at predetermined locations.
Ingenious Design Process
The ingenious design process allows researchers to mix and match 300 different DNA staples, each with a unique sequence, enabling the assembly of complex structures with remarkable ease. The exterior of these voxels can be tailored with additional DNA strands, creating programmable sites that allow for further construction of sophisticated patterns and shapes, all observable under an electron microscope.
Implications and Future Research
As the researchers continue to refine their methods and expand their capabilities, the implications of their work extend infinitely into medicine, material science, and robotics. Will we soon see a world where tiny robots are routinely used in medical treatments and environmental responses? The future seems bright, and it all starts with a tiny dinosaur. Stay tuned for more thrilling developments from the world of nanotechnology!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)