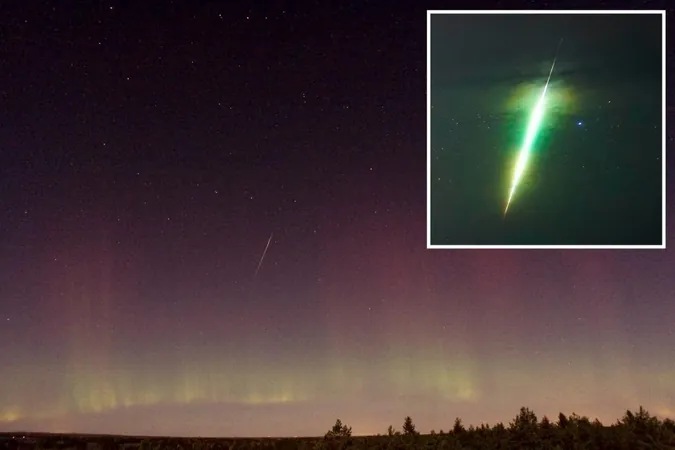

Don't Miss the Draconid Meteor Shower: A Cosmic Event You Must See Before 2025!
2024-10-06
Author: Chun
Introduction
The Draconid meteor shower is lighting up the night sky once again, and while this year's display may not be as dazzling as in some past years, astronomers are buzzing with excitement about a potential spectacular show in 2025. This annual event, which runs from October 6 to October 10, offers a unique opportunity for stargazers, especially those in areas with low light pollution.
Viewing Expectations
Although the Draconids are known for being fickle, viewers can expect to see about 10 meteors per hour during the peak viewing on the evenings of October 7 and 8. What makes the Draconids so intriguing is their unpredictability. Unlike more consistent meteor showers, they can sometimes deliver bursts of activity, with intense outbursts leading to over 1,000 meteors an hour. Although this year's viewing might be underwhelming compared to those rare spectacular resets, industry experts caution that the cosmic dragon may awaken once more in 2025, making it a potentially jaw-dropping experience.
Preparation for Viewing
Gathering some friends, a cozy blanket, and a thermos of hot cocoa are essential components for a successful meteor-watching night, especially when considering the key factors for viewing success: crystal-clear skies, minimal light interference, and preparedness for late-night adventures.
Nature of the Draconids
NASA's Bill Cooke aptly describes the Draconids as an "all-or-nothing shower." Without an outburst, the typical Draconid display can yield only two to three meteors per hour—definitely a faint show for those expecting a firework spectacular. This year’s faint display is largely due to the shower's slow-moving nature, as they travel at a relatively mellow speed of 21 kilometers per second.
Cosmic Influences
What determines the intensity of the meteor shower varies significantly depending on gravitational interactions. Cooke notes the influence of Jupiter, whose gravitational pull can alter the trajectory of the comet that generates the Draconids. This interplay can lead to either an exhilarating viewing experience or a subdued show, depending on how the comet interacts with other celestial bodies.
Spotting Draco
If you're keen on spotting Draco, the constellation from which these meteors emerge, you'll find it conveniently positioned near the prominent Big Dipper and Little Dipper. With its distinctive shape, Draco is relatively easy to locate for amateur astronomers.
Origins of the Draconids
The origins of the Draconids date back to the winter of 1900, with their discovery attributed to French astronomer Michel Giacobini at Nice University. Ernst Zinner later played a pivotal role in their recovery in 1913. These meteors originate from the comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner, which releases trails of rock and ice, igniting in the atmosphere to create the mesmerizing celestial display.
Conclusion
So, gather your loved ones and mark your calendars, because witnessing the Draconid meteor shower is a cosmic event that should not be missed. Stay tuned for 2025, as it promises to bring a stunning night of shooting stars, igniting the skies once more!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)