Earth's Inner Core Discovered to be "Rotating Backwards" – What This Means for Our Planet!
2025-03-31
Author: Jia
Introduction
In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists have found that Earth's inner core is undergoing drastic changes, including a phenomenon described as "rotating backwards." This striking discovery, highlighted in a recent study published in Nature Geoscience, has ignited intense discussion among geophysicists about the complex dynamics within our planet’s interior.
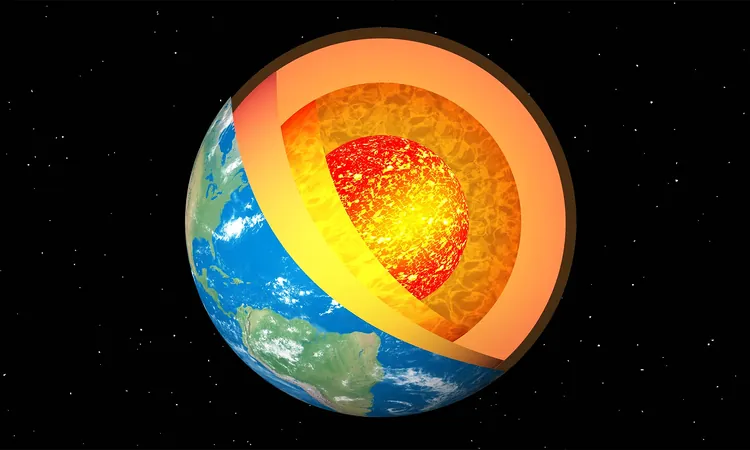
The Inner Core
Located over 3,000 miles beneath the Earth’s surface, the inner core is a solid sphere primarily composed of iron. Although smaller than the Moon, it plays a pivotal role in generating Earth's magnetic field. Recent research indicates that significant changes may have begun around 2010, with evidence suggesting that the inner core's rotation has not only slowed drastically but has also reversed its direction relative to the Earth's surface.
Research Methodology
Utilizing seismic signals from earthquakes across the globe, researchers have been able to probe the inner core, which is encased in a fluid outer core made of swirling liquid metal. This innovative approach involved analyzing data from 121 repeating earthquakes recorded near the South Sandwich Islands from 1991 to 2023, combined with historical data from Soviet and French nuclear tests conducted in the 1970s.
Expert Insights
John Vidale, a leading geophysicist at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, emphasized the magnitude of this finding: "When I first analyzed those seismograms, I was perplexed. But once we identified multiple observations revealing the same pattern, the conclusion was undeniable."
Findings of the Research
The research revealed "unambiguous evidence" of this slowing trend since 2010, indicating that the inner core is now rotating at a speed that is slightly less than the rotation of the Earth itself. Vidale noted that the dynamics at play are influenced significantly by the flow of the liquid iron in the outer core, which generates the planet’s magnetic field. These fluid movements and gravitational forces from the overlying mantle are believed to have potential impacts on day length—though any changes would be minuscule, on the order of a thousandth of a second.
Implications of the Findings
The new findings enhance our understanding of the inner core's behavior, suggesting it undergoes structural transformations over time due to interactions with the outer core. While previous studies hinted at the notion of a reversing core, the current research presents solid evidence that the core’s motion is not static but rather dynamic.
Future Research Directions
As scientists strive to refine their understanding of these intricate behaviors, they aim to track the inner core's rotation and shape over coming decades more precisely. By doing so, they may uncover the underlying forces driving these shifts, offering insights that might connect fluctuations in the planet’s magnetic field and other geological phenomena back to the inner core.
Conclusion
This research not only transforms our understanding of the Earth’s inner workings but also raises exciting questions about the potential impacts of such changes on climate and geological stability. The ongoing analysis of seismic waves will continue to provide invaluable glimpses into a world deep underground that has long remained shrouded in mystery.
The full study details will be available in the upcoming editions of scientific journals, paving the way for further research opportunities in this fascinating field.
Stay tuned as we explore more about what this revelation means for our planet's future!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)