
Everything You Need to Know About October's Stunning 'Ring of Fire' Solar Eclipse
2024-10-01
Prepare yourself for a mesmerizing celestial display!
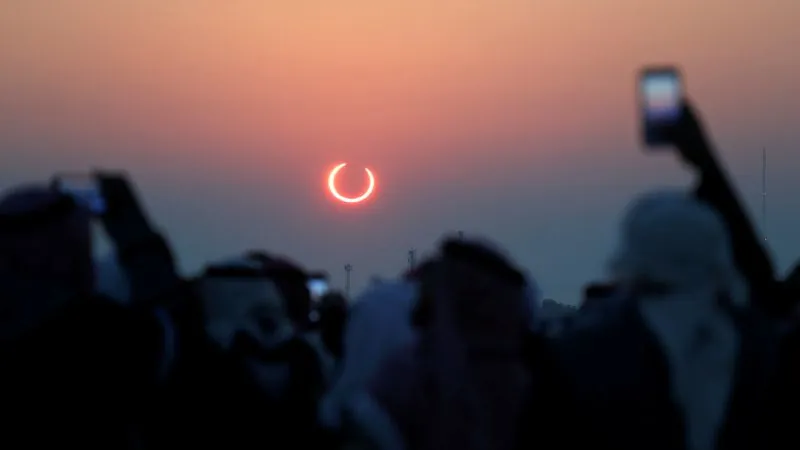
This Wednesday, an incredible annular solar eclipse will grace the skies, creating a breathtaking "ring of fire" effect that will be visible from parts of South America. According to NASA, this astronomical event is bound to leave sky-gazers in awe.
What is an Annular Solar Eclipse?
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon positions itself directly between the Earth and the sun. However, when the moon is at its farthest point from Earth, it appears smaller in the sky and cannot fully obscure the sun's bright light. Instead, a glowing ring, often described as a "ring of fire," encircles the dark silhouette of the moon, offering a stunning visual treat.
Where and When to See It
This particular eclipse will traverse over the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, reaching remote locations such as Rapa Nui (Easter Island) and parts of Argentina and Chile. Those in clear skies within these areas will be in for a spectacular view. The annular eclipse is scheduled to kick off at 12:50 p.m. ET and wrap up by 4:39 p.m. ET, peaking at approximately 2:45 p.m. ET, when the ring of fire will be at its most prominent for over seven minutes.
Path of the Eclipse
Starting over 1,056 miles southwest of Hawaii, the eclipse will touch down on land first at Rapa Nui at 3:07 p.m. ET, with a captivating ring lasting for 6 minutes and 23 seconds. The spectacle will then progress to locations like the Patagonian coast of Chile at 4:22 p.m. ET and briefly appear in Argentina shortly thereafter.
For those not directly in the path of the annular eclipse, a partial eclipse will be visible from various locations including Hawaii, parts of Mexico, and even down to New Zealand and Uruguay, so be sure to check local listings for specifics.
Safe Viewing Tips
Safety is paramount during such celestial events. Never look directly at the sun without proper eclipse glasses or handheld solar viewers, as doing so can cause irreversible eye damage. Certified eclipse glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful rays, and regular sunglasses are simply not sufficient.
If you lack appropriate glasses, you can still enjoy the eclipse indirectly. Options include making a pinhole projector or using items you may have at home—a colander, straw hat, or even your hands with fingers spaced apart will work. Just remember to position yourself so that you're not looking directly at the sun.
Mark Your Calendars for Upcoming Celestial Events
Once this eclipse wraps up, the sky will continue to put on shows throughout the year! Watch for the hunter’s moon—a supermoon—on October 17, followed by the beaver moon on November 15, and the cold moon marking the year’s final full moon on December 15.
Additionally, meteor shower enthusiasts should prepare for October's Draconids (7-8) and Orionids (20-21), followed by holiday season meteor showers including the Geminids (13-14) and Ursids (21-22).
Get ready to embark on a celestial adventure—secure your eclipse glasses, find a great viewing spot, and don’t forget to enjoy these awe-inspiring moments in the cosmos!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)