Groundbreaking Study Reveals Surprising Impact of Covid Lockdowns on Moon's Temperature!
2024-09-29
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Surprising Impact of Covid Lockdowns on Moon's Temperature!
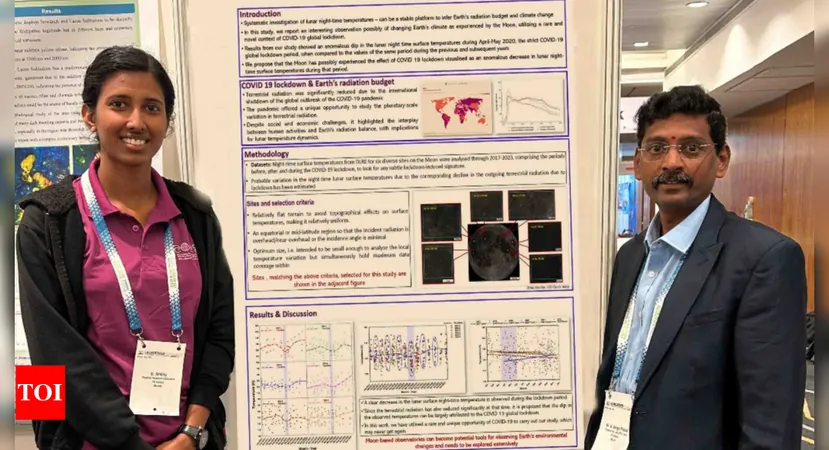
In a fascinating revelation, Indian researchers have determined that the global Covid-19 lockdowns of 2020 may have actually led to an unexpected drop in lunar surface temperatures. A peer-reviewed study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters indicates that the Moon experienced a significant dip of 8-10 Kelvin during the peak of the lockdowns, specifically from April to May 2020. This remarkable finding suggests that changes in human activity on Earth can extend their influence far beyond our planet.
The research, spearheaded by K Durga Prasad and G Ambily from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) in Bengaluru, analyzed nighttime surface temperatures at six key sites on the Moon's nearside over a six-year span from 2017 to 2023. Through meticulous investigation, they utilized data from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and discovered a consistent temperature decrease in 2020 compared to the same time frame in previous years.
PRL director Anil Bharadwaj praised the team's work, calling it "quite unique" and highlighting its significance in the scientific community. The researchers attribute the observed temperature drop to a reduction in Earth's outgoing radiation linked to decreased human activities—resulting in less greenhouse gas emissions and aerosols, and consequently, less heat retention in Earth's atmosphere.
The data presents a telling narrative: during 2020, the Moon recorded its coldest temperatures at various sites, contrasting sharply with a noticeable warming trend in 2021 and 2022, after human activities returned to normal. For instance, the lowest temperature observed, a chilling 96.2 Kelvin, occurred at one site in 2020, while the highest recorded low was 143.8 Kelvin in 2022.
Prasad articulated the importance of these findings, stating, "The Moon acts as an amplifier of Earth's radiation signature. This global event provided us with a rare opportunity to observe how changes in human activity can impact our nearest celestial neighbor." The researchers did consider other possible influences, such as solar activity and seasonal variations, but concluded that these factors did not significantly alter their findings.
While this research unlocks an intriguing correlation between Earth's climate and lunar surface temperatures, the authors emphasize the need for further studies to solidify this connection. They propose that future lunar observatories could play a pivotal role in monitoring Earth’s climate changes, leveraging the Moon as a natural laboratory for environmental studies.
This study not only accentuates the interconnectedness of celestial bodies but also serves as a reminder of the unforeseen effects human activities have on our environment, both on Earth and beyond. Stay tuned for more updates as researchers delve deeper into this extraordinary phenomenon!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)