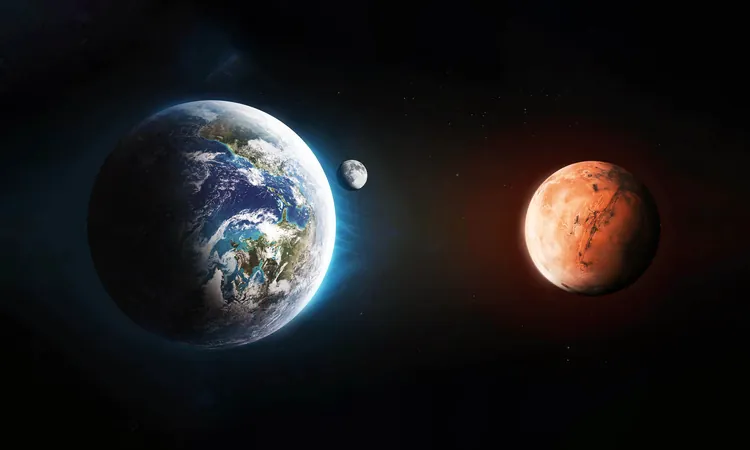

Shocking Connection Between Mars' Gravity and Earth's Climate Revealed!
2024-12-09
Author: Wai
Recent groundbreaking research has unveiled a stunning link between the gravitational field of Mars and the climate of Earth, adding a new layer to our understanding of how celestial forces influence our planet.
Evidence collected over the last 65 million years indicates that Earth experiences deep-sea current cycles that fluctuate in strength approximately every 2.4 million years. These cycles, termed “astronomical grand cycles,” may be intricately connected to the gravitational interactions between Mars and Earth.
Mars’ Gravitational Influence
As both Mars and Earth cruise through the solar system, they exert gravitational forces on one another, causing subtle but significant changes known as gravitational perturbations. Despite the vast distances that often separate them—tens of millions of miles—the gravitational pull between these two planets can impact each other's orbits ever so slightly.
When Mars and Earth are at their closest point during an event known as opposition, which occurs roughly every 26 months, these tiny nudges can lead to alterations in Earth’s orbital shape and tilt over extended periods. Such shifts can, in turn, influence long-term climatic patterns on our planet.
How Gravitational Interactions Affect Climate
The study indicates that these gravitational effects not only affect the orbital dynamics but also play a role in the strength of Earth’s deep-sea currents. The vigorous movement of these currents is crucial for sediment distribution across the ocean floor. During periods of enhanced current strength—often characterized as giant whirlpools—there's significant sediment erosion, particularly at abyssal depths.
Contributors to this study, including Dietmar Müller from the University of Sydney, emphasize that the gravitational fields of planets interact in ways that modify their orbital eccentricity, changing how circular or elliptical their orbits are. Due to this resonance with Mars, Earth’s orbit may be slightly drawn closer to the Sun, thereby increasing solar radiation and raising global temperatures.
Importantly, researchers made extensive use of satellite data to trace sediment accumulation over millions of years, learning that warmer ocean conditions, influenced by Mars's gravity, may have led to disruptions in sediment deposition.
What Are the Implications of These Findings?
These findings hold significant implications. They may help sustain vital ocean currents like the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which is essential for regulating Earth's climate by transporting warm water from the tropics to the colder Northern Hemisphere. As scientists growingly express concern over the potential collapse of such currents due to climate change, this research suggests that gravitational effects could prevent stagnation in oceanic systems even if temperatures rise drastically.
The intricate dance of orbital mechanics underscores the relationship between planetary movements and Earth’s weather systems. Moreover, understanding how gravitational interactions shape our climate over millions of years could enhance our responses to current climate challenges.
Mars and Its Cosmic Role
Despite its smaller size and mass—resulting in only 38% of Earth's gravitational strength—Mars still exerts a notable influence, not only on Earth but on its own moons, Phobos and Deimos. These moons are slowly spiraling inward due to Mars’ gravitational field and are predicted to eventually break apart, forming a ring around the planet.
The significance of Mars’s gravitational pull extends to the operation of spacecrafts that utilize gravity assists for maneuvers aimed toward distant objectives, illustrating how interconnected celestial bodies influence one another through gravitational forces.
This compelling research is a reminder of how the cosmos shapes our climate and provides insight into the ocean's resilience amid ongoing climate transformations. The findings emphasize that while we grapple with the realities of human-induced climate change, ancient celestial mechanics continue to drive changes in our planet’s natural systems.
This groundbreaking study has been published in the journal *Nature Communications*, shedding light on the grand cosmic ballet and its unexpected effects on Earth's environment.
Stay tuned, as this extraordinary exploration of the universe's impact on our planet reveals just how little we may know about the intricate connections that bind us to our celestial neighbors!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)