Shocking Discovery: "Darkness" — A New Alien Predator Unearthed in the Ocean's Abyss!
2024-12-12
Author: Jia
Introduction
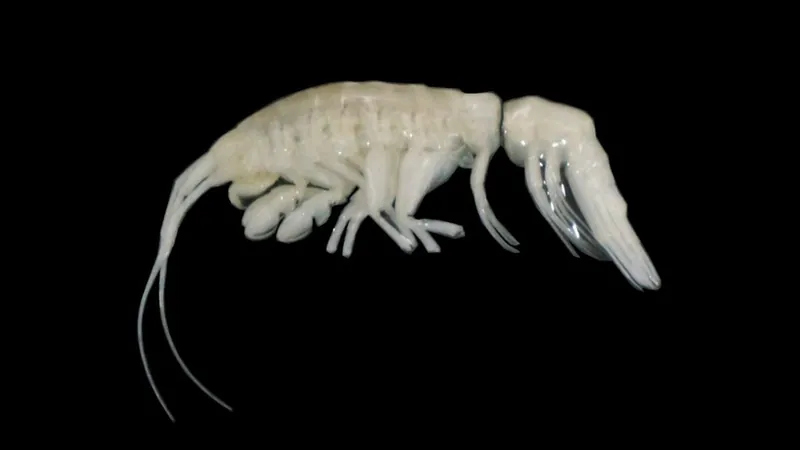
The deep ocean, long regarded as one of the planet's final frontiers, continues to astonish scientists with its revelations. Recent research has unveiled an extraordinary new species of amphipod, dubbed **Dulcibella camanchaca**, which was discovered at a remarkable depth of **7,902 meters** in the **Atacama Trench**, situated off the coasts of Peru and Chile.
Naming and Significance
The name "camanchaca," translating to "darkness" in indigenous languages of western South America, perfectly encapsulates the enigmatic nature of this newly identified creature. This discovery not only enhances our understanding of deep-sea biodiversity but also emphasizes the significance of unexplored regions of our oceans.
The Expedition
During the **2023 Integrated Deep-Ocean Observing System (IDOOS) Expedition**, scientists braved the treacherous conditions of the hadal zone, which spans from **6,000 to 11,000 meters** beneath the surface. These depths are notoriously difficult to study due to extreme pressures and darkness, yet they house some of the planet's most specialized and unique species.
Atacama Trench Characteristics
The **Atacama Trench** is particularly noteworthy for its isolation and high sedimentation rates. This distinctive environment fosters the evolution of life in ways that remain largely unknown, with several species identified as endemic to the trench, such as various amphipods, snailfish, and even the intriguingly named mud dragon.
Dulcibella camanchaca's Role in the Ecosystem
Dulcibella camanchaca, with its elegant body structure, adds to the expanding catalog of unique species residing in this trench. This predatory amphipod belongs to the **Eusiridae** family, encompassing other deep-sea predatory species scattered across oceanic trenches worldwide. Its discovery marks the first time this amphipod has been classified into a new genus, a significant advancement in our understanding of deep-sea ecology.
Predatory Behavior of Amphipods
What sets predators like Dulcibella camanchaca apart from their scavenger counterparts is their predatory behavior. These amphipods actively hunt for smaller organisms, thus playing an essential role in regulating the deep-sea food web. As stewards of their ecosystems, their presence helps maintain the delicate balance crucial for the survival of many species within these dark expanses of ocean.
Conclusion
As exploration into these depths continues, who knows what other alien creatures await discovery? Scientists are eager to unearth more surprises that could redefine our comprehension of marine biology and the intricate tapestry of life hidden beneath the waves. Stay tuned; the deep ocean may hold more secrets than we ever imagined!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)