The Rising Tide of Dementia: A Looming Crisis
2025-01-13
Author: Lok
Introduction
The latest projections reveal startling statistics about the impending burden of dementia in the United States. With the older population witnessing its most rapid growth between 2010 and 2020, the need to address dementia’s escalating prevalence has never been more urgent. The most troubling aspect? The lifetime risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease, is expected to rise dramatically in the coming decades.
Demographic Changes and Challenges
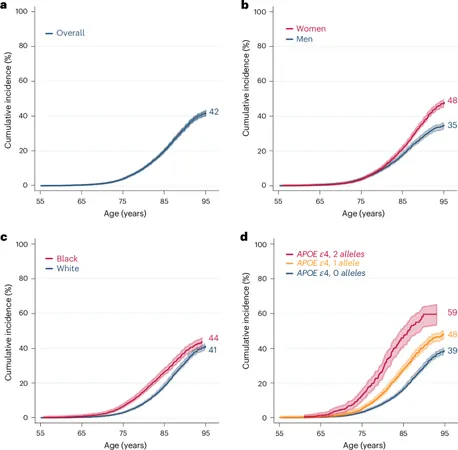
According to the US Census Bureau, the older population of the United States expanded at a rate not observed since the late 19th century, presenting a significant challenge for healthcare systems nationwide. As the number of elderly individuals increases, so too does the incidence of age-related disorders, especially Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Current estimates from 2020 indicate that millions of Americans are facing these debilitating conditions, with expectations that by 2060, these numbers could surge into the millions more.
Factors Contributing to Dementia Risk
Recent studies shed light on critical factors that contribute to the risk of dementia. Research shows that lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and even hearing health, can significantly affect cognitive decline. Interventions that focus on multifactorial approaches, such as the FINGER study, which combines diet, exercise, cognitive training, and monitoring vascular risks, have demonstrated promising results in preventing cognitive decline in at-risk older adults.
Socioeconomic and Genetic Influences
Moreover, socioeconomic factors, racial disparities, and genetic predispositions—particularly involving the apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene—play crucial roles in determining individual risk levels for dementia. Studies indicate that individuals with certain genetic markers have a heightened risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, highlighting the need for personalized prevention strategies.
Gender Differences in Dementia Risk
Gender differences also emerge in the narrative of dementia. Research has consistently shown variances in incidence and prevalence between men and women, suggesting that sex hormones and other biological factors could contribute to disparities in dementia risk. This calls for further exploration into sex-specific treatment approaches.
Economic Impact and Policy Implications
As the healthcare landscape grapples with these challenges, the cost of care associated with dementia continues to escalate. Projections indicate that the financial burden of Alzheimer's and other dementias could reach unprecedented levels, creating critical implications for policymakers. The Lancet Commission on Dementia emphasizes the importance of prevention and early intervention strategies to mitigate costs and improve quality of life for those affected.
Conclusion
Overall, the evolving landscape of dementia underscores an urgent public health challenge that requires immediate attention. Governments, healthcare providers, and communities must collaborate to develop comprehensive strategies that not only address the medical facets of dementia but also incorporate lifestyle modifications and awareness campaigns to combat this growing crisis.
Call to Action
Stay informed about dementia trends and preventive measures—the future of our aging population depends on it.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)