Unraveling a Cosmic Enigma: Jupiter's Magnetic Tornadoes and Their Astonishing Impact on the Gas Giant's Poles
2024-12-06
Author: Kai
Introduction
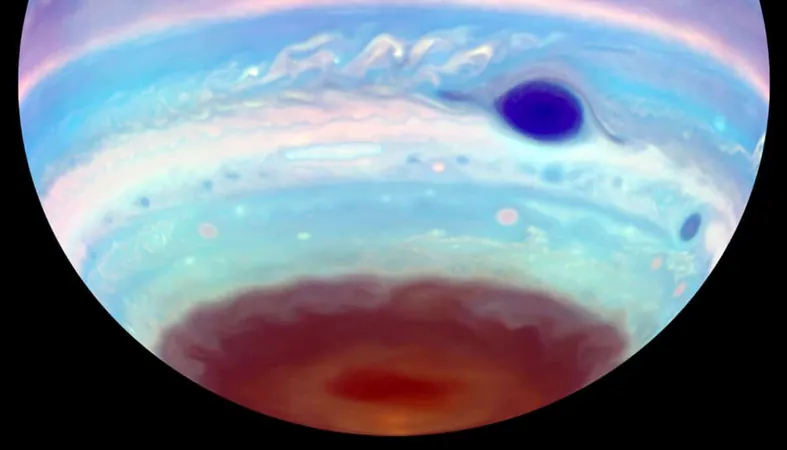
In a groundbreaking discovery that could change our understanding of Jupiter's atmosphere, researchers have identified Earth-sized dark ovals that shimmer in ultraviolet (UV) light. These elusive spots, which emerge and disappear unpredictably, provide a unique insight into the dynamic behaviors of Jupiter's atmosphere.
Observations and Discovery
At the South Pole, dark UV ovals can be observed 75% of the time, while their counterparts in the North Pole are visible in only 12.5% of images captured, indicating a stark contrast in atmospheric phenomena across the gas giant. These oval formations, comparable in size to Earth, are situated just below the brilliant auroral zones that light up Jupiter's atmosphere.
Imaging Techniques
What’s particularly striking is that these dark patches are only revealed through advanced imaging techniques like those employed by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. Their dark appearance suggests intricate processes linked to Jupiter's immense magnetic field, which penetrates deeper parts of the atmosphere than what we see with Earth's auroras.
The Role of Magnetic Tornadoes
The mysterious dark ovals were initially detected back in the late 1990s, but their significance has only recently come to light through a detailed study conducted by undergraduate researcher Troy Tsubota from UC Berkeley. By meticulously analyzing Hubble images, Tsubota uncovered their frequency and patterns, shedding light on Jupiter's atmospheric behavior.
Formation of Dark Ovals
Researchers have theorized that the formation of these dark ovals is closely linked to an extraordinary atmospheric phenomenon known as magnetic tornadoes. These tornado-like vortices emerge from friction between Jupiter’s magnetic field lines, occurring in two distinct places: the ionosphere, where unusual spinning motions occur, and the hot plasma sheet surrounding the planet, which is heavily influenced by the volcanic activity of its moon, Io.
Impact on Jupiter's Atmosphere
These magnetic tornadoes churn the thick gases in Jupiter's atmosphere, much like tornadoes on Earth disturb air currents. While these tornadoes dissipate as they plunge deeper into the atmosphere, they leave behind substantial clouds of gas, creating the dense UV-dark ovals identified by astronomers.
Broader Implications
The implications of this research extend far beyond Jupiter itself. The insights gathered on Jupiter's atmospheric layers, where haze density in the dark regions is an astonishing 50 times thicker than in the surrounding areas, could help scientists understand the atmospheric processes in other gas giants and beyond, including exoplanets orbiting distant stars.
Dynamic Changes
Moreover, findings suggest that these ovals form relatively quickly, taking about a month to develop and only a couple of weeks to dissipate, indicative of an ever-changing dynamic atmosphere on the gas giant.
Conclusions
The interplay between different atmospheric layers around Jupiter highlights an intricate web of forces that govern not only our solar system’s largest planet but also offers clues to the broader dynamics of planetary systems. Ultimately, studies like this underscore the significance of long-term observational projects, such as the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL), which enable astronomers to monitor and track changes in the atmospheres of gas giants throughout time.
Future Exploration
As we continue to unlock the mysteries of Jupiter, one of our solar system's most enigmatic worlds, tantalizing questions remain about the nature of its storms and magnetic features, posing a thrilling frontier for future explorations in planetary science.






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)