A Rare Brain Abscess in China: The Shocking Role of Helcococcus kunzii
2025-04-12
Author: Li
A Disturbing Medical First
In a startling case reported in November 2023, a 54-year-old woman from China sought treatment after suffering from dizziness, headaches, and vomiting for ten days. Her condition took a dark turn when a local hospital's CT scan revealed a mysterious intracranial lesion. Despite managing hypertension with self-medication, she had no known habits like smoking or drinking that could complicate her health. This case would soon unveil a shocking medical mystery.
Severe Symptoms and Confounding Diagnosis
Upon her arrival at the Neurology Department, the patient's condition showed alarmingly high blood pressure of 199/104 mmHg, and mental status changes raised immediate concerns. Laboratory results indicated elevated inflammatory markers, sending medical staff into high alert.
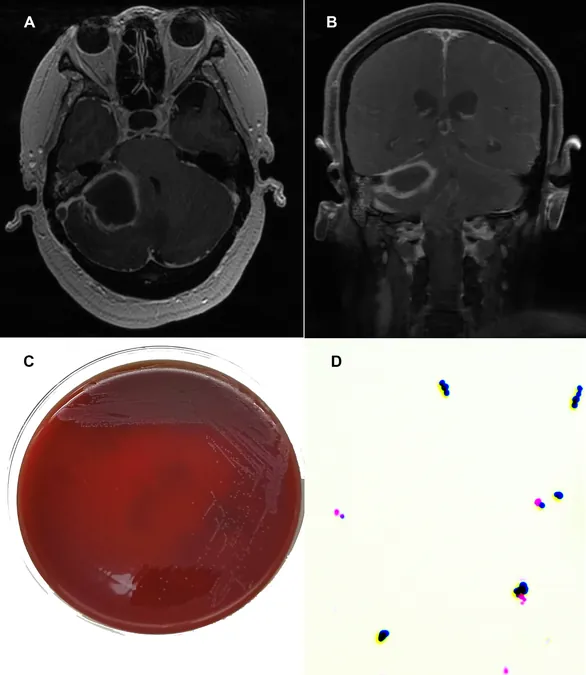
Unexpected MRI Findings
MRI scans on November 21 revealed circumferential enhancement in the cerebellopontine angle, hinting at a potentially infectious abscess. The scans indicated issues in the right middle ear and mastoid, signaling a connection to her tympanitis. Critically, subsequent imaging highlighted a dangerous venous sinus thrombosis, escalating her case to a surgical emergency.
Surgery and Its Perils
Urgent surgical intervention was necessary, and on day four, doctors performed an occipital lobectomy. During the operation, an abscess capsule was uncovered, and concerns over a possible anaerobic infection were raised. Swift actions included the initiation of intravenous antibiotics to counter the lurking infection.
The Bacterial Culprit Revealed
Microbial tests later exposed the primary invader: Helcococcus kunzii. Known since 1993, this unusual bacterium had previously been linked to cases in immunocompromised patients but had never before been tied to a brain abscess from tympanitis. Its presence, paired with a polymicrobial infection, underscored the complexity of her condition.
A History of Neglect and New Insights
Despite H. kunzii’s past as a skin commensal, this rare case reinforces its emerging profile as a dangerous opportunistic pathogen, especially in individuals with prior medical issues. Notably, nearly a third of previous cases involved additional infectious agents, complicating treatment outcomes.
Breaking New Ground in Diagnosis
This incident marks China’s first brain abscess case linked to H. kunzii, highlighting the need for awareness in clinical settings. The patient, after extensive treatment and surgery, demonstrated remarkable recovery without significant abnormalities at follow-up.
The Path to Recovery and Future Vigilance
Given this groundbreaking case, medical professionals must prioritize advanced diagnostic tools like MALDI-TOF MS and genetic sequencing to identify obscure pathogens like H. kunzii rapidly. Continuous surveillance of resistance patterns will be crucial as this bacterium proves to be a formidable adversary in infections.
Conclusion: A Warning for the Medical Community
This astonishing case serves as a wake-up call for medical communities worldwide to acknowledge and prepare for the threats posed by rare pathogens like H. kunzii. Its neuroinvasive potential could signify more severe challenges ahead, making vigilance and rapid diagnosis ever more critical.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)