Alarming Decline in Global Freshwater Levels Uncovered by NASA Satellites
2024-11-17
Author: Arjun
Groundbreaking Discovery by Researchers
An international team of researchers has made a groundbreaking discovery using data from NASA and German satellites: the Earth's total freshwater resources have experienced a significant and alarming decline since May 2014. This startling information, reported in *Surveys in Geophysics*, suggests that our planet may have entered a prolonged dry phase that could have drastic implications for the environment and humanity.
Satellite Observations and Findings
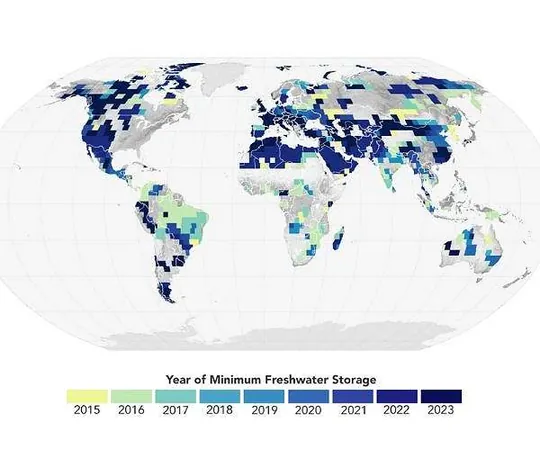
From 2015 to 2023, satellite observations revealed that freshwater reserves on land—including lakes, rivers, and underground aquifers—have plummeted by 290 cubic miles (approximately 1,200 cubic kilometers). This staggering figure is equivalent to two and a half times the volume of Lake Erie. Matthew Rodell, a hydrologist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, emphasized the severity of these losses, which could exacerbate existing challenges related to water scarcity.
Severe Implications for Freshwater Supply
The implications of this dwindling freshwater supply are severe. During prolonged droughts, urban areas and agricultural regions are increasingly leaning on groundwater, which is being depleted faster than it can be replenished. This unsustainable reliance not only threatens the water supply for communities but also puts farmers at risk, potentially leading to famine, conflict over resources, economic instability, and public health crises due to reliance on contaminated water sources. A 2024 UN report highlights the escalating risks associated with global water stress, an urgent issue that demands immediate attention.
Technology Behind the Discovery
The research team leveraged data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites to identify the global freshwater deficit. These satellites measure minute fluctuations in the Earth's gravity, reflecting changes in water mass above and below the surface. The original GRACE satellites operated from March 2002 until October 2017, paving the way for their successors, the GRACE-FO satellites, launched in May 2018.
Drought and Global Impacts
The drastic decline in global freshwater began with a severe drought in northern and central Brazil, quickly followed by significant droughts across Australasia, North America, Europe, and Africa. The phenomenon was exacerbated by one of the most powerful El Niño events since 1950, which altered weather patterns around the globe. Despite the conditions stabilizing post-El Niño, freshwater levels have failed to recover, with Rodell noting that 13 of the most intense droughts recorded worldwide since January 2015 highlight the ongoing crisis. There are growing suspicions that global warming is a catalyst for this enduring reduction in water availability.
Climate Change and its Connection
As the planet warms, the atmosphere retains more water vapor, contributing to extreme precipitation events. However, this does not always translate to steady groundwater supplies; instead, long dry intervals often precede these heavy downpours, preventing soil from absorbing water effectively. NASA meteorologist Michael Bosilovich explained that as temperatures rise, both the evaporation of surface water increases and the atmosphere's capacity to hold water grows—both of which intensify drought conditions globally.
Uncertainties and Looking Forward
While there are indicators that the current drop in freshwater is linked to climate change, experts assert that definitive connections remain elusive. Hydrologist Susanna Werth from Virginia Tech, who was not part of the study, pointed out the inherent uncertainties in climate models and predictions, emphasizing the complexity of establishing direct causation.
Conclusion and Urgency for Action
Looking ahead, the fate of global freshwater levels remains uncertain. Will they rebound to pre-2015 levels, stabilize, or continue their downward trend? Given that the nine hottest years recorded align with the period of freshwater decline, Rodell asserts, "We don’t believe this is a coincidence; it could be a sign of dire consequences to come." As the situation develops, the world must stay vigilant and adaptable to ensure sustainable management of its precious water resources amid these alarming and unprecedented changes.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)