Alarming Insights: Factors Impacting Survival Rates of HIV-Positive Adults Undergoing Antiretroviral Therapy in Eastern Ethiopia Revealed!
2024-11-27
Author: Ming
Introduction
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) continues to be a major health crisis worldwide, leading to thousands of deaths every year, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) has proven effective in prolonging lives, yet mortality rates remain strikingly high during the initial years following treatment initiation. A recent study targeting HIV-infected adults in Jigjiga, Eastern Ethiopia, sheds light on the survival rates and critical predictors of mortality for these patients from 2015 to 2021, emphasizing the urgent need for targeted interventions.
Research Overview
The study utilized a retrospective analysis of data collected from three governmental hospitals in Jigjiga, specifically analyzing patient records from January 2015 to December 2021. It aimed to uncover both survival probabilities and the factors affecting mortality rates among adults starting ART.
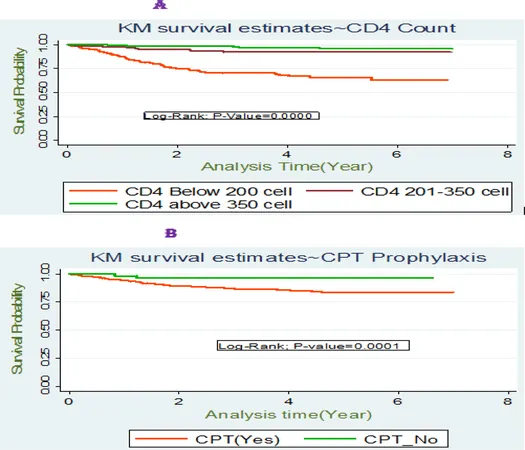
Key Findings
The study's findings are stark. Out of 842 participants, nearly 11% succumbed to HIV-related illnesses, with a notable mortality incidence rate of 3.92 deaths per 100-person years of observation. The overall survival probability stood at around 83.97%, a figure that raises significant concerns given the ongoing global battle against HIV/AIDS.
Noteworthy predictors of mortality identified in the study included: - **Advanced WHO Stage III/IV**: Patients at advanced stages of HIV exhibited more than double the risk of mortality. - **Caregiver Presence**: Those without a caregiver had a 2.23-fold increase in mortality risk. - **Functional Status**: Bedridden patients were found to have a 2.18 times higher chance of death compared to those deemed capable of working. - **Adherence Levels**: A poor adherence level to ART was linked to a staggering 4.23-fold increase in mortality risk, highlighting the importance of adherence to therapy.
Exploring the Bigger Picture
These findings reflect a broader trend unfolding in the fight against HIV/AIDS, where success is contingent not just on medication but also on social support structures and awareness of treatment protocols. The study confirms what many experts have noted: social and psychological factors play a crucial role in treatment success.
Globally, as of the most recent statistics, approximately 40.1 million individuals have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the onset of the epidemic. ART access has increased significantly, yet adherence remains a major hurdle, particularly in low and middle-income countries, including Ethiopia, where stigma and social issues persist.
Significance of This Study
This study plays a vital role in informing healthcare policies and programs designed to improve outcomes for people living with HIV. Recognizing the high mortality rates associated with advanced disease stages and poor adherence emphasizes the need for comprehensive approaches that include psychological support, community education, and improved healthcare access.
In conclusion, to combat HIV-related mortality effectively, it is crucial to enhance caregiver support, encourage consistent treatment adherence, and ensure timely initiation of ART at early disease stages. As Ethiopia launched its universal "Test and Treat" initiative back in 2015, continuous improvement and tailored interventions in the healthcare system are necessary steps toward achieving better survival rates among HIV-infected individuals.
Call to Action
The world must double down on efforts to destigmatize HIV, ensuring individuals feel empowered to seek timely treatment and support. By working together, we can change the narrative surrounding HIV and its impact on communities facing this health crisis, paving the way toward healthier futures for millions.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)