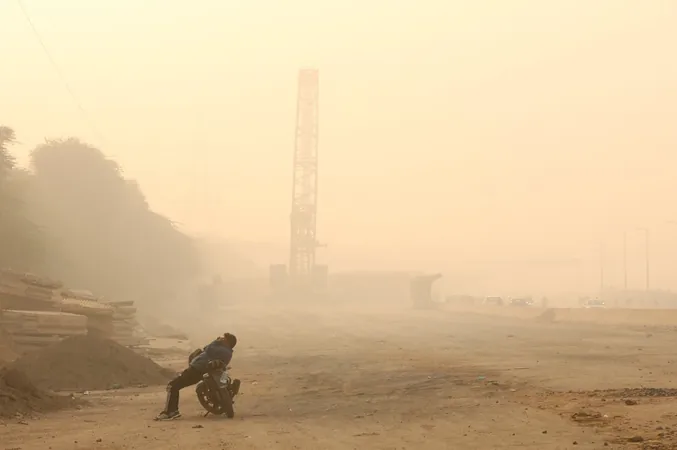

Alarming Link Between Air Pollution and Surge in Lung Cancer Deaths
2024-11-18
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
Lung cancer continues to be one of the deadliest cancers around the globe, and new research reveals a striking connection between rising air pollution levels and increasing mortality rates from this aggressive disease. Recent findings illustrate that a staggering 18.56% of lung cancer deaths can be traced back to air pollution, underscoring an urgent public health crisis exacerbated by environmental factors.
The Growing Threat of Outdoor Air Pollution
Outdoor air pollution—primarily fueled by industrial activities, urbanization, and human behavior—has been shown to heighten the risk of lung cancer by approximately 10%. As we move through November, designated as Lung Cancer Awareness Month, health advocates are seizing this opportunity to spotlight the dual threats posed by tobacco use and environmental pollutants.
Staggering Health Consequences Stemming from Air Pollution
According to the 2022 Black Report released by the Clean Air Rights Platform (THHP), air pollution is a significant contributor to mortality in Türkiye, resulting in 68,440 deaths linked to pollution-induced health conditions in just one year. The report identified a spectrum of diseases connected to poor air quality, including cardiovascular ailments, respiratory diseases, various forms of cancer, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Key Contributors of Air Pollution
Deniz Gümüşel, coordinator of the THHP, identifies key sources of air pollution: fossil fuel combustion, industrial emissions, waste management practices, construction, and agricultural activities. Alarmingly, air pollution is recognized as the second leading global risk factor for premature death according to the World Health Organization's Global Burden of Disease Study, contributing to nearly 50% of deaths from Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), along with significant percentages from heart disease and strokes.
A Call to Action for Cleaner Air
Gümüşel asserts that these public health risks are largely preventable. Immediate efforts are needed to phase out fossil fuels, regulate industrial emissions, enhance public transportation options, and adopt urban planning initiatives that prioritize clean air.
Gender Disparities and Outdoor Air Pollution's Threat
Dr. Pınar Akın Kabalak, president of the Lung Cancer Working Group at the Turkish Respiratory Research Association (TÜSAD), notes that women may be particularly vulnerable to air pollution's adverse effects. Factors like smaller lung volumes and a higher tendency to engage in indoor cooking activities expose them to indoor air pollution risks. Additionally, the reliance on fossil fuels for cooking and heating in poorly ventilated homes in lower-income communities exacerbates health threats.
Kabalak highlights that specific pollutants, such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide, significantly elevate lung cancer risks, with long-term exposure potentially increasing risk by as much as 8%. While lung cancer is under intense scrutiny due to its mortality rate, environmental pollution is recognized as a formidable foe in the fight against this disease.
Proactive Strategies to Mitigate Risks
Several strategies have emerged to combat the burgeoning risks associated with air pollution:
1. Quit Smoking: Tobacco use remains the leading cause of lung cancer; cessation is the most effective defense against the disease.
2. Ensure Safe Building Materials: Communities must verify that construction materials are free from toxic substances like asbestos. Government regulation of indoor air quality, particularly in older structures, is crucial.
3. Forest Fire Prevention: Outdoor activities in fire-sensitive zones should be carefully managed to minimize wildfire impacts on air pollution.
4. Safety Standards for High-Risk Workers: Adherence to health and safety regulations in industries like mining, construction, and agriculture is vital. Proper protective equipment and regular inspections can significantly mitigate pollutant exposure.
5. Diligent Monitoring of Pollution Sources: Governments are urged to keep a close eye on industries contributing to pollution and enforce stricter regulations to limit their environmental footprint.
As the shadow of lung cancer looms larger, it is imperative that individuals, communities, and governments alike unite in addressing the unsettling reality of air pollution and its role in this public health crisis. Taking proactive measures today could lead to a healthier tomorrow for countless individuals around the world.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)