Alarming Rise of Drug-Resistant Infections: The Deadly Reality of Acinetobacter baumannii in Northeast Iran
2024-10-04
Author: Siti
In-Depth Look at Nosocomial Infections
In the complex landscape of modern healthcare, the threat of nosocomial infections looms large, escalating the risks for hospitalized patients. One particularly menacing bacterium is Acinetobacter baumannii, notorious for its resistance to conventional antibiotics, including carbapenems. This study delves into its prevalence, risk factors, and the dire clinical outcomes associated with it in Gorgan, Iran, from 2016 to 2018.
Methods and Findings: A Closer Look at the Data
The study employed a retrospective cross-sectional design, analyzing the medical records of 143 patients diagnosed with Acinetobacter baumannii infections in two institutions. By dissecting variables such as demographics, reasons for hospitalization, underlying health conditions, and previous antibiotic treatments, the researchers were able to uncover critical trends.
The grim statistic emerges: 25.87% of patients succumbed during hospitalization, with markedly higher mortality rates observed in infants and individuals aged 45-65 years. Alarmingly, being unmarried significantly increased the risk of death, representing a structured social support deficiency among patients.
Furthermore, hospitalization in Intensive Care Units (ICU) was marked as a significant risk factor, elevating the mortality rate. The resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii were shown to correlate with increased fatalities—a crucial finding in light of the rising global challenge of multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens.
Underlying Causes: The Perfect Storm
The prevalence of Acinetobacter baumannii infections is especially prevalent in settings where antibiotics are overused and infection control measures are insufficient. According to the World Health Organization, developing countries face a compounded risk due to systemic issues such as poor healthcare standards, malnutrition, and inadequate access to effective medications.
Moreover, Acinetobacter baumannii is an opportunistic pathogen that can thrive on hospital surfaces, evading decontamination efforts and infecting vulnerable patients. It's often implicated in various infections, including pneumonia and bloodstream infections, raising alarms for healthcare providers worldwide.
Key Insights and Recommendations
The study underscores the urgent need for improved infection control protocols and effective antimicrobial stewardship programs. It highlights the importance of rigorous adherence to hygiene protocols and timely antibiotic interventions based on susceptibility testing to mitigate the impact of these drug-resistant bacteria.
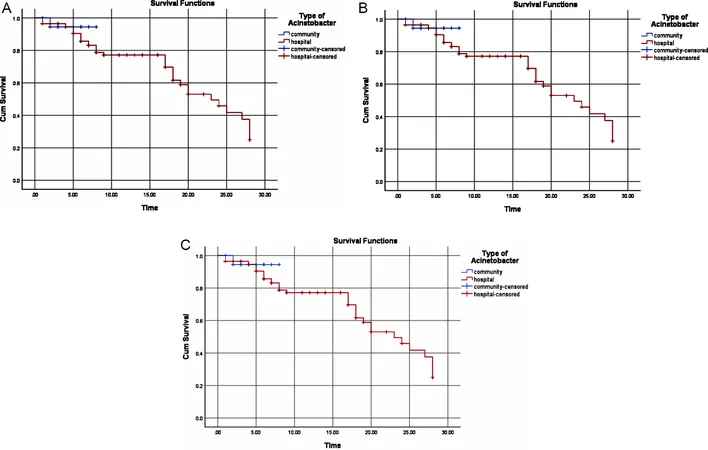
Interestingly, the findings suggest that community-acquired infections present a lower risk of mortality compared to hospital-acquired infections, signaling the pressing need for targeted interventions in the latter.
To illustrate the severity of the situation, the survival rate for patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii was significantly lower, averaging just over 12 days, compared to 23 days for those with susceptible strains. This stark contrast emphasizes the critical need for effective initial treatment strategies to enhance patient survival outcomes.
Looking Ahead: The Call for Action
As healthcare systems aim to combat the relentless threat of antibiotic resistance, continuous research and surveillance are paramount. Effective educational programs for healthcare practitioners about infection control practices and antibiotic prescribing are essential.
Furthermore, regional and global collaboration to share epidemiological data can play a transformative role in managing and potentially reversing the tide of antibiotic resistance. As documented in this study, the clinical implications are profound, and immediate actions are required to safeguard patients from the deadly grip of drug-resistant infections.
In summary, the findings from Gorgan illuminate a pervasive health crisis that demands urgent attention, innovative solutions, and collaborative efforts to eradicate the threats posed by drug-resistant pathogens. If left unaddressed, the consequences will echo beyond the walls of hospitals, impacting public health on a global scale.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)