Alarming Surge: Chikungunya and Dengue Viruses Co-Circulate in Brazil's 2023 Outbreak
2024-11-20
Author: John Tan
Overview of the Study
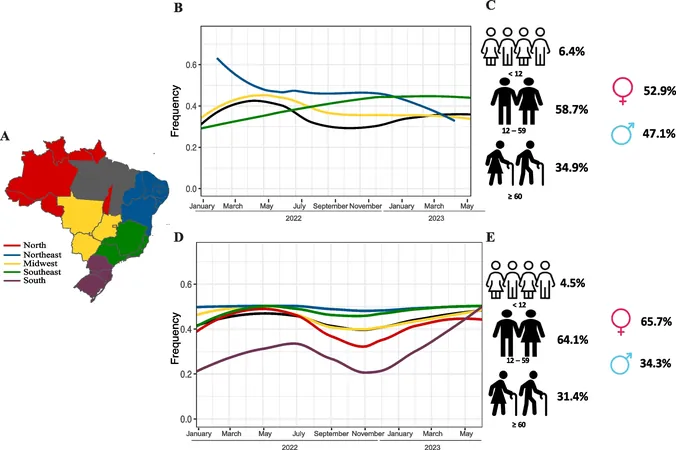
This research, approved by the Research Ethics Committee, analyzed over 66,000 samples for CHIKV and 157,000 samples for DENV across the country from January 2022 to June 2023. Conducted at the Hermes Pardini Institute, the study revealed that regions most affected include the Southeast and Northeast, where laboratory units are densely concentrated.
Escalating Numbers: Data Breakdown
The nationwide positivity rates for both viruses have been alarming. For CHIKV, the positivity rate soared to 43.9% in 2023, with significant regional disparities: the Southeast recorded a staggering 47.4% positivity rate, while the Northeast followed with 24.2%. The total number of confirmed cases of CHIKV spiked remarkably from 10,765 in 2022 to 62,542 in 2023, alongside an increase in mortality from 2 to 33 deaths.
DENV also exhibited troubling numbers, with confirmed cases escalating from 73,648 in 2022 to a startling 260,316 in 2023, resulting in 165 deaths and highlighting a concerning trend of severe cases of the virus.
Regional Insights and Demographics
The state of Minas Gerais (MG) witnessed particularly striking trends in the incidence of these arboviruses, primarily influenced by climatic factors favorable for the breeding of mosquito vectors. Spatiotemporal analysis traced the rapid spread of conditions conducive to outbreaks, emphasizing the risk of transmission across borders, especially with neighboring states like Bahia where the viruses were first introduced.
Notably, the data showed that women accounted for 65.7% of CHIKV cases and a similar disproportionate share of DENV cases, with children under 12 comprising a concerning percentage of total infections—6.4% for CHIKV and 12.5% for DENV.
Coinfections and Genomic Data
An important aspect of the research was the investigation into co-infections. About 12.75% of DENV-positive samples were also infected with CHIKV, indicating a complex interplay between these viruses. Genomic sequencing identified distinct strains of CHIKV and DENV; notably, most DENV samples belonged to serotype 1.
Researchers also highlighted specific non-synonymous mutations in the CHIKV genomes that could suggest evolving strains with implications for transmissibility and virulence.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Given the alarming rise in case numbers and mortality rates, the study underscores an urgent need for public health measures focusing on vector control, vaccination, and widespread screening. As Brazil prepares for another season of heightened risk due to arboviruses, immediate action is required to mitigate further outbreaks. The intricate relationship between these viruses, the demographic patterns revealed, and the genomic findings all point to a dire need for a comprehensive and robust response strategy in combating these diseases.
As citizens become aware of these disquieting trends, the health authorities must escalate efforts to communicate risks and preventive measures to the public. Could Brazil be on the brink of a full-blown arbovirus crisis? Only time will tell, but the signs are undeniably ominous.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)