Battle of Treatment: Surgical vs Conservative Approaches for Perianal Abscess in Blood Cancer Patients
2025-04-11
Author: Wei Ling
Understanding Perianal Abscess in Hematologic Malignancies
A recent study conducted at Fujian Union Hospital analyzed the effectiveness of surgical and conservative treatments for patients suffering from perianal abscesses and hematologic malignancies over a seven-year period. The findings shed light on a pressing medical issue affecting a vulnerable patient demographic.
What Exactly is a Perianal Abscess?
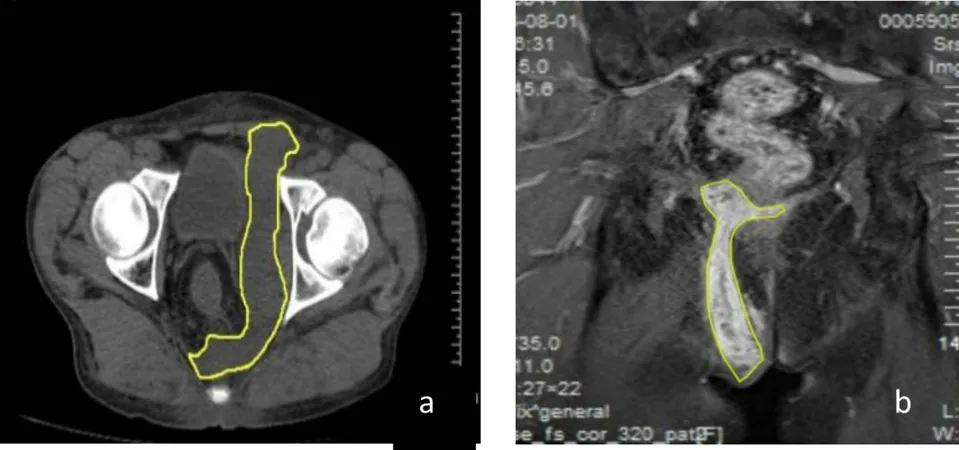
A perianal abscess is characterized by a painful, swollen mass around the anus that can be a serious complication for individuals with hematologic conditions like leukemia and lymphoma. This study included patients aged 18 and older who were diagnosed with perianal abscesses, ensuring a stringent evaluation process with thorough medical records.
Treatment Strategies: A Closer Look
Participants were split into two groups: those undergoing surgical interventions and those receiving conservative treatment. Surgical approaches included: 1. **Incision and Drainage:** Commonly performed under local or spinal anesthesia, this method involved making an incision to drain pus and promote healing while avoiding complications like anal stenosis. 2. **Seton Placement for Complex Cases:** For more complex abscesses involving fistulas, a silicone tube was placed to ensure continuous drainage and avoid damage to surrounding tissues.
In the Conservative Corner
Patients in the conservative group were treated with antibiotics and local care, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans. This method also included regular assessments based on clinical progress, with the antibiotic treatments tailored to the results from microbial cultures.
Examining Treatment Outcomes
Over the course of the study, notable clinical outcomes were observed. Out of 53 patients, 90.5% demonstrated significant improvement, while some experienced complications, including two distinct cases of necrotizing fasciitis. This highlights the critical nature of timely and appropriate treatment.
Microbial Insights from the Abscesses
The study also detailed the microbial landscape of the abscesses, uncovering a predominance of Gram-negative bacteria such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Remarkably, many of these pathogens exhibited antibiotic resistance, complicating treatment efforts.
Who Came Out on Top?
Despite the observable differences in recovery times, especially with conservative treatment showing quicker results, no significant differences in cure rates between the two groups were found. The surgical group exhibited a slightly lower recurrence rate, offering a glimmer of hope for those prone to repeated infections.
Gender Disparity in Perianal Abscesses
Interestingly, the study revealed a significant male predominance among patients. This aligns with existing data suggesting males are statistically more prone to perianal abscesses, though the reasons behind this gender disparity remain unclear.
Final Thoughts and Future Directions
Overall, the study emphasizes the delicate balance in treating perianal sepsis among patients with hematological malignancies. With both treatment methodologies proving to be viable, there is an urgent call for more extensive research to define clearer protocols and optimize patient outcomes.
As the medical community works toward better treatment pathways, understanding the complexities of perianal infections in immunocompromised patients will be vital in shaping future care strategies. This comprehensive analysis could pave the way for more personalized and effective treatment approaches.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)