
Breakthrough Discovery: Aspirin and Other Anti-Inflammatories Could Revolutionize Cancer Immunotherapy!
2024-11-28
Author: Sarah
Introduction
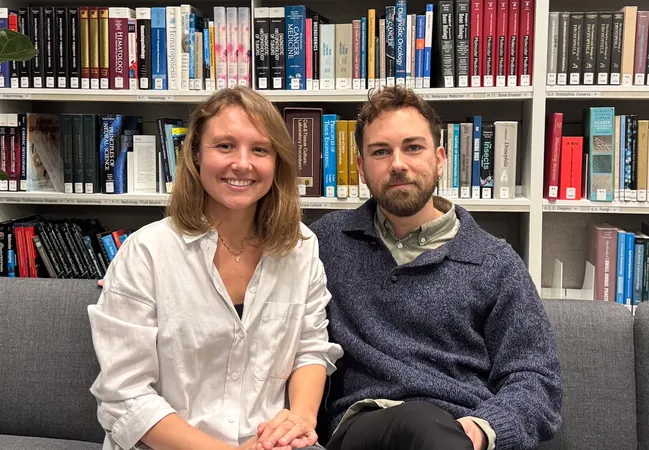
A groundbreaking study conducted by two young Spanish scientists, Anais Elewaut and Guillem Estivill, has uncovered a potential game-changer in cancer treatment—specifically for enhancing immunotherapy—by leveraging common anti-inflammatory medications like aspirin. This discovery builds upon the monumental work of immunotherapy pioneers Tasuku Honjo and James Allison, who have transformed cancer treatment since Honjo's identification of the PD-1 protein in 1992.
The Challenge of Resistance
Immunotherapy has already provided new hope to countless cancer patients by allowing their immune systems to recognize and effectively battle tumors. However, resistance remains a formidable challenge; more than 50% of metastatic melanoma cases do not respond to current immunotherapy drugs. The research team from the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology in Vienna has discovered that the addition of anti-inflammatories significantly heightens the efficacy of these treatments.
Research Findings
In a series of experiments involving genetically modified mice, the researchers found that those treated with both immunotherapy and anti-inflammatories showed remarkable improvements, with some subjects achieving complete remission. Estivill stated, "Without the anti-inflammatory, these mice were resistant to immunotherapy," emphasizing the need for this combination to unlock the full potential of the treatment.
Role of Monocytes
The study reveals that monocytes, another type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the activation of killer T cells—the body’s frontline defenders against cancer. When monocytes capture fragments of cancer cells and present them to T cells, an immune response is triggered, but tumor cells have developed mechanisms to evade this process. They produce prostaglandin E2, which inhibits monocyte function and dampens immune responses.
Potential of Anti-Inflammatories
By using anti-inflammatories like aspirin that inhibit the action of cyclooxygenase, the researchers postulate that it may be possible to enhance the immune system's ability to combat cancer. Estivill noted that other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen could offer similar benefits based on retrospective analyses of clinical trials, where patients taking these medications showed improved outcomes.
Cautions and Future Directions
However, the researchers caution that while anti-inflammatories may delay cancer progression, they are not a standalone cure. Their work suggests a multi-faceted approach which entails combining immunotherapy, controlled doses of anti-inflammatories, and potentially other immune-stimulating drugs.
The Human Translation Challenge
It's essential to recognize that while early results in animals are promising, human tumors are markedly more heterogeneous, making it uncertain whether these strategies will translate directly to human patients. Elewaut warned against viewing aspirin as a miracle cure, urging caution due to the potential side effects associated with high doses of NSAIDs, such as gastrointestinal and cardiovascular issues.
Expert Opinions
The laboratory's leader, Anna Obenauf, emphasizes that aspirin is just one of several options under investigation. Moreover, alternatives like celecoxib, a more targeted drug used for arthritis relief, are already in clinical trials, suggesting that the future could hold even more effective treatments on the horizon.
Community Response and Outlook
The scientific community is enthusiastically receiving these findings, as noted by Marisol Soengas, president of the Spanish Association for Cancer Research. Soengas praised the rigorous methodology of the study while cautioning that it will take time to determine how the findings will affect standard cancer treatment protocols.
Conclusion
As research continues, the hope is that such combinations could offer a beacon of hope for cancer patients facing dire prognoses, radically improving the landscape of cancer treatment and paving the way toward more personalized, effective therapies. Stay tuned as the journey towards enhanced immunotherapy unfolds!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)