Breakthrough Discovery in Alzheimer’s Research: Astrocytes Hold the Key to New Treatment!
2024-09-30
Author: Jia
Breakthrough Discovery in Alzheimer’s Research: Astrocytes Hold the Key to New Treatment!
A groundbreaking study led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has unveiled a promising new mechanism to combat Alzheimer’s disease (AD), potentially changing the landscape of treatment. The research team, collaborating with experts from the Institute for Basic Science and Boston University, has identified a therapeutic target within astrocytes—non-neuronal cells in the brain that could play a critical role in managing one of the most devastating neurodegenerative diseases.
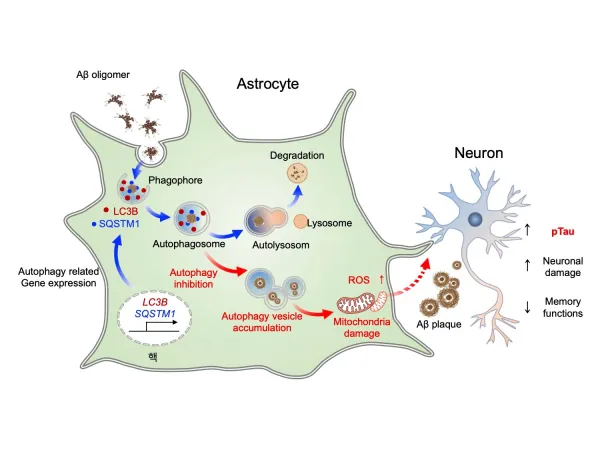
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the accumulation of toxic proteins, namely amyloid-beta (Aβ) oligomers, that disrupt neuronal function. These protein clusters lead to inflammation and neuronal damage, ultimately manifesting as cognitive decline and memory loss. Despite extensive research, the intricacies of how astrocytes contribute to this process remained elusive—until now.
The study reveals that astrocytes are capable of initiating autophagy, a vital cellular process that detoxifies and recycles damaged components. When inflammation or protein buildup occurs in the AD-afflicted brain, astrocytes respond by activating specific genes related to autophagy. The team demonstrated that enhancing these autophagic pathways within astrocytes could significantly reduce the presence of toxic Aβ aggregates and restore cognitive functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s.
Notably, the activation of autophagy-associated genes within astrocytes located in the hippocampus—a region of the brain that governs memory—was particularly effective. This discovery is groundbreaking as it shifts the focus from traditional neuron-centered strategies in Alzheimer's treatments and highlights astrocytes as a potential therapeutic target.
Dr. Ryu, along with first author Dr. Suhyun Kim, emphasizes the importance of understanding how enhancing astrocytic functions can restore neuronal health. “Our findings demonstrate that targeting astrocytic autophagy could be a game changer in our approach to Alzheimer’s treatment, paving the way for innovative drug developments aimed at harnessing this cellular mechanism,” said Dr. Ryu.
The implications of this research extend beyond just treatment; it opens the door for preclinical studies aimed at developing drugs that can bolster astrocytic autophagic activity, potentially preventing or mitigating dementia symptoms. As we face an increasing prevalence of Alzheimer's worldwide, this discovery could herald a new era of neuroscience, shifting the paradigm of how we approach disease management.
With KIST’s commitment to pioneering innovative research, and ongoing support from the Korean government, the path ahead looks promising for Alzheimer’s disease research. Stay tuned, as this could be the breakthrough we've all been waiting for!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)