Breakthrough Discovery: Scientists Unveil a ‘Toolkit’ to Repair DNA Damage Linked to Aging and Cancer!
2024-11-21
Author: Wei Ling
Groundbreaking Study by Sheffield and Oxford Universities
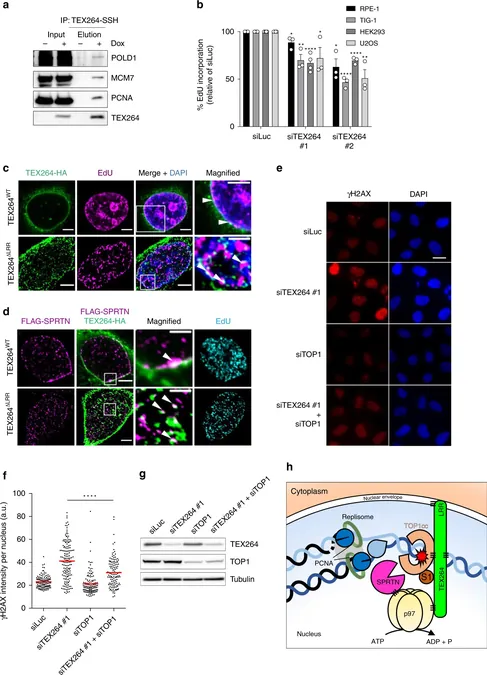
In a groundbreaking new study, scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Oxford have revealed a remarkable “toolkit” designed to repair damaged DNA, which is closely linked to aging, cancer, and motor neuron disease (MND). This exciting breakthrough could pave the way for innovative treatments that may significantly enhance healthspan and combat various diseases.
Discovery of TEX264 Protein
Published in the prestigious journal *Nature Communications*, the research identifies a critical protein known as TEX264, which, along with other specialized enzymes, can recognize and eliminate harmful proteins that adhere to DNA, leading to its damage. Such damaged DNA accumulation is a major contributor to cellular aging and conditions like cancer and neurological disorders, including MND.
Implications for Cancer Treatment
For years, the mechanisms of repairing this type of DNA damage remained elusive, but this discovery offers new hope. Researchers are optimistic about leveraging this novel toolkit of proteins to develop strategies that could safeguard against aging-related ailments, cancer, and debilitating neurological diseases.
Targeting TEX264 in Chemotherapy
Additionally, the findings have significant implications for chemotherapy. This standard cancer treatment intentionally introduces DNA breaks to destroy malignant cells; however, targeting the TEX264 protein may represent a safer and more effective approach to cancer therapy. STRATEGY ALERT: Researchers envision that enhancing TEX264's function could revolutionize cancer treatment while minimizing adverse effects.
Expert Insights
Professor Sherif El-Khamisy, Co-Founder and Deputy Director of the Healthy Lifespan Institute at the University of Sheffield, emphasizes, “Failure to repair DNA breaks within our genome can greatly diminish our ability to live a healthy life into old age and render us susceptible to conditions like Motor Neuron Disease. By comprehending how our cells mend DNA breaks, we are taking significant steps towards addressing these health challenges, along with exploring novel cancer treatments.”
Co-researcher Professor Kristijan Ramadan from the University of Oxford shared his enthusiasm about the implications of this discovery. “Our identification of TEX264 as a key player in the cellular machinery that cleanses toxic proteins from DNA radically alters the existing knowledge of DNA repair processes, potentially shielding us from accelerated aging, cancer, and neurodegeneration.” He expressed pride in his team’s pioneering work that unveiled TEX264’s role in DNA repair and underscored the ongoing commitment to exploring cancer therapies that harness this finding.
Looking Forward
As researchers continue their groundbreaking work, the scientific community and cancer patients alike eagerly await the next steps. This discovery not only marks an essential advancement in understanding cellular mechanisms but also sparks hope for future therapies that could change the landscape of treatment for age-related diseases and cancer. Keep an eye on these developments – the future of medicine may just be on the horizon!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)