Breakthrough in Immune Defense: How Our Body's Proteins Battle Bacteria Revealed!
2024-10-11
Author: Ming
Introduction
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery regarding our body's natural defense mechanisms against harmful pathogens. The protein GBP1 has been identified as a crucial player in our innate immune system, serving as a frontline soldier in the battle against bacteria and parasites. This remarkable discovery sheds light on the previously unknown mechanisms by which GBP1 encases pathogens in a protective coat, enhancing our understanding of immune responses.
Research Publication
A team of researchers at Delft University of Technology has published their findings in the prestigious journal *Nature Structural & Molecular Biology*. Their work could revolutionize the development of new medications and therapies, particularly for individuals with compromised immune systems.
Role of Guanylate Binding Proteins
According to biophysicist Arjen Jakobi, Guanylate Binding Proteins (GBPs) are essential in fending off numerous infectious diseases. He highlights how these proteins combat ailments such as dysentery, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, and even sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia. Importantly, they also play a role in preventing toxoplasmosis, a severe risk for pregnant women and their unborn children.
Mechanism of Action
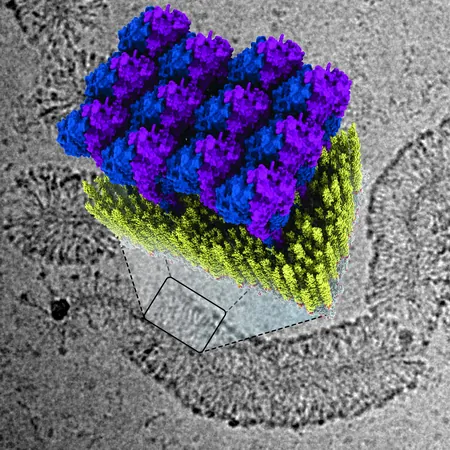
In this pivotal study, Jakobi and his team unveiled the intricate process through which GBP1 proteins target and neutralize bacterial threats. Lead author Tanja Kuhm, a Ph.D. candidate in Jakobi’s lab, describes how GBP1 envelopes bacteria, effectively tightening its grip until the bacterial membrane is compromised. This breach allows immune cells to eliminate the infection more efficiently.
Advanced Research Techniques
To achieve this remarkable insight, the researchers utilized advanced technologies, including cryogenic electron microscopy, to examine the binding interactions between GBP1 proteins and bacterial membranes at a molecular level. This innovative approach gave them a detailed three-dimensional view of how the protective protein coat forms.
Significance of the Research
Jakobi emphasizes the significance of this research in enhancing our understanding of how the immune system combats bacterial infections. He suggests that if we can effectively manipulate these proteins through targeted medications, it may open the door to new strategies for accelerating recovery from various infections.
Future Implications
This research not only highlights the complex workings of our immune defenses but also paves the way for potential therapeutic advancements. As the scientific community continues to explore the intricacies of GBP1 and its role in immune response, we may soon see breakthroughs that could transform treatment options for millions suffering from infectious diseases. Stay tuned—this discovery could be a game-changer in the fight against infections!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)