
Breakthrough in Solar Storm Predictions: How India's Aditya-L1 Mission is Revolutionizing Protection for Power Grids and Satellites
2024-11-28
Author: Daniel
Introduction
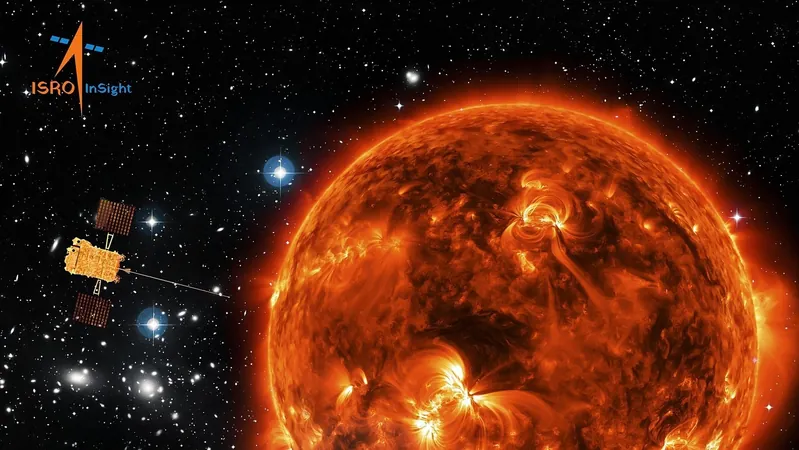
The groundbreaking Aditya-L1 solar mission is changing the game for Earth's technological infrastructure by providing vital data that could shield power grids and satellites from the devastating effects of solar storms.
Launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) earlier this year, the Aditya-L1 spacecraft has already demonstrated its capabilities by successfully detecting the onset of a coronal mass ejection (CME), a colossal eruption of charged particles emitted by the Sun. This advancement promises to enhance early warning systems for solar storms, known to create significant disruptions in power supplies, satellite communications, and even navigation systems worldwide.
Named after the Hindu sun god, Aditya, this mission is now part of an elite cadre of solar observatories alongside those operated by renowned agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). Orbiting beyond the interference of Earth's atmosphere, Aditya-L1 provides an unobstructed constant view of solar activity, free from the limitations posed by eclipses and other terrestrial obstructions.
The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
CMEs can unleash up to a trillion kilograms of solar material, racing toward Earth at speeds reaching 3,000 kilometers per second. They cover the vast 150-million-kilometer stretch from the Sun to our planet in a mere 15 hours. When these eruptions collide with Earth’s magnetic field, they can induce geomagnetic storms, leading to blackouts, GPS inaccuracies, and damage to satellites. The recent successful detection of a CME by Aditya-L1 exemplifies its potential to timely identify and track these solar disturbances.
How the Velc Instrument Plays a Crucial Role
At the heart of this mission's success is the Velc instrument, a sophisticated coronagraph that mimics a solar eclipse. Unlike ground-based observatories, which often fail to detect subtle solar phenomena, Velc effectively blocks the Sun's blinding inner layers, allowing the delicate outer corona to be observed. This unobstructed view enables Aditya-L1 to continuously monitor solar activities and detect CMEs from their inception. The remarkable capacity to provide early warnings can offer critical lead time for infrastructure to mitigate the adverse impacts of these solar storms.
Conclusion
As the Aditya-L1 mission progresses, its findings are set to bolster the resilience of Earth’s power grids and satellite systems, ultimately ensuring a more stable technological environment. Stay tuned for more updates as this innovative endeavor unfolds and reshapes our understanding of solar dynamics!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)