Breakthrough Neural Network Models Transform Predictions of Immunotherapy Success in Small Cell Lung Cancer!
2024-10-11
Author: Siti
Introduction
As immunotherapy revolutionizes the treatment landscape for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), the ability to predict patient outcomes is becoming increasingly crucial in clinical settings. Following rigorous clinical trials, immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy has emerged as the first-line treatment option, showcasing significant survival advantages. Nevertheless, accurately forecasting its effectiveness has remained a daunting task due to the lack of reliable biomarkers.
Groundbreaking Study Overview
A groundbreaking study published in *Malignancy Spectrum*, titled "Neural Network Models Based on Clinical Characteristics for Predicting Immunotherapy Efficacy in Small Cell Lung Cancer," leverages advanced deep-learning techniques to develop an innovative predictive model, aiming to serve as a robust decision-making tool for clinicians.
Research Methodology
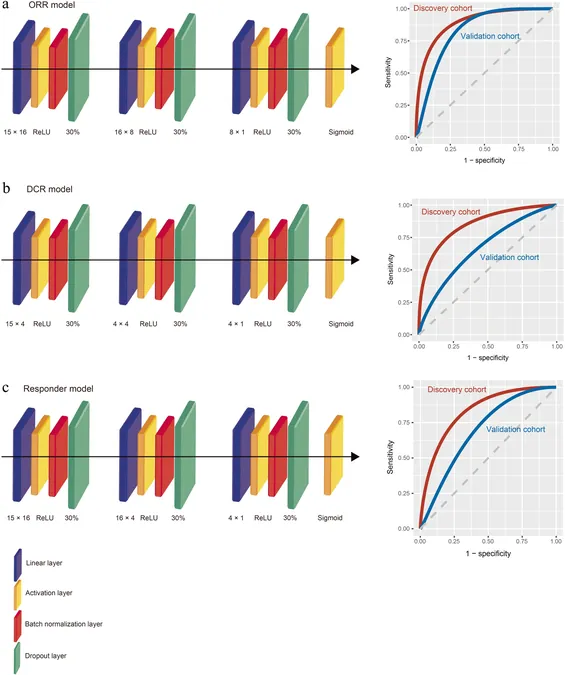
In their investigation, researchers retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 140 SCLC patients who received immunotherapy. The participants’ data were carefully divided into a discovery cohort and a validation cohort. Through the construction and training of neural network models, the team successfully developed predictive models that assess three key clinical outcomes: the Objective Response Rate (ORR), the Disease Control Rate (DCR), and the likelihood of patients achieving Progression-Free Survival (PFS) for over six months.
Results
Remarkably, the results indicated that the ORR model achieved an impressive Area Under the Curve (AUC) value of 0.8964 in the discovery cohort and 0.8421 in the validation cohort, revealing a high level of predictive accuracy. To enhance user accessibility, these models have been condensed into a tool designed with clinicians in mind.
Implications of the Research
This pivotal research not only introduces valuable scientific insights for personalizing treatment plans for SCLC patients but also lays the groundwork for informed and effective clinical decision-making surrounding immunotherapy approaches. The findings open the door to tailored therapies that could significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Future Directions
Moreover, the research team has expressed their commitment to refining the model further. They plan to conduct extensive prospective studies involving multiple centers and larger sample sizes to validate the model’s stability and applicability across diverse patient populations.
Conclusion
As the potential of neural networks continues to unfold in oncology, this advancement holds the promise of ushering in a new era of personalized cancer care—one where patients benefit from tailored treatments that are predictively optimized for success! Stay tuned for more updates on how technology is transforming cancer treatment.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)